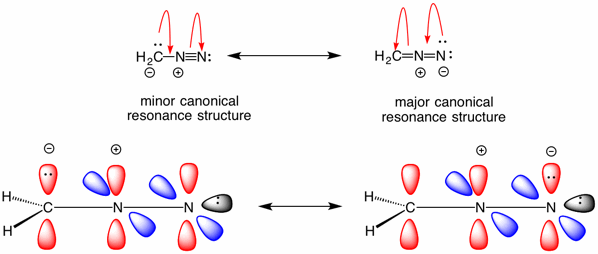
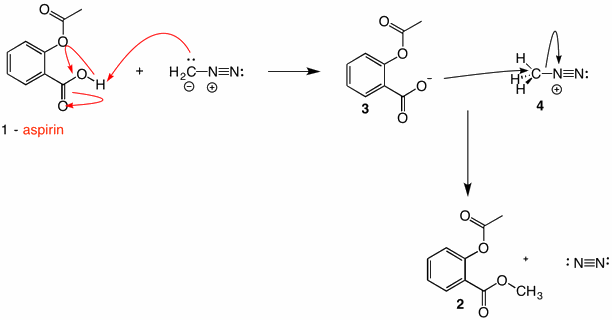
Solution:
Diazomethane is a planar, resonance stabilized compound with negative charge on both the carbon and the terminal nitrogen. A positive charge resides on the central nitrogen. Most of the negative charge exists on nitrogen which is better able to stablize negative charge than carbon. [See the electrostatic potential map of diazomethane here.] Protonation on nitrogen is a non-productive event. However, protonation on carbon leads to species 4, which is an exceptionally reactive electrophile because the leaving group is nitrogen. The carboxylate ion effects an SN2 displacement to produce the methyl ester 2 of aspirin. Note that in this reaction both oxygens of the ester are supplied by the carboxylic acid where as Fischer esterification of a carboxylic acid and a primary alcohol each supply one oxygen apiece. The use of tertiary alcohols in the Fischer esterification with a carboxylic acid is similar to the diazomethane reaction in regard to the oxygens. Click here.