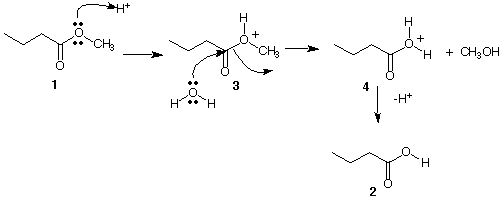
Ester 1:
Solution
There are two mechanisms for this reaction that can be considered.
Mechanism A is similar to an SN2 displacement wherein protonated species 3 undergoes displacement by water to give methanol and protonated 4. Loss of the proton gives butyric acid. The cycle is catalytic in H+.

Mechanism B involves protonation of the carbonyl oxygen of 1 followed by addition of water to form tetrahedral intermediates 5 and 6. Reprotonation of 6 at the methoxy oxygen followed by elimination of methanol leads to 2 via 7.
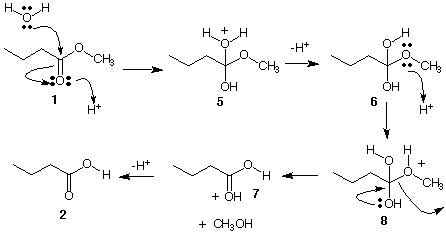
Which mechanism is correct? Here are the facts. Hydrolysis with O18 water results in the incorporation of O18 in the carbonyl oxygen of unhydrolyzed ester 1 and O18 evenly distributed in each oxygen of carboxylic acid 2. Think about it then click here.