In 1840, Christian Friedrich Schönbein (1799-1868) discovered ozone (Gr.; odorant), the sharp odor produced by electrical discharges. Seven years later (1847) he observed that ozone oxidizes organic compounds but not to their ultimate products of oxidation, carbon dioxide and water. [Two years prior, he had spilled nitric and sulfuric acid on his Frau's apron in her kitchen. The apron, made of cotton, combusted and thus was discovered gun cotton, nitrocellulose. Schönbein also observed that hydrogen peroxide (Threnard; 1818) is oxidized to oxygen gas in the presence of hemoglobin. ] In the period 1903-1916, Carl Dietrich Harries (1866-1923), an assistant to both Hofmann (of the eponymous elimination and rearrangement) and Fischer (of projection and carbohydrate fame) at Berlin, published some 80 papers on the reactions of ozone with organic compounds. His interest was stimulated by the reaction of ozone with rubber, a process that causes rubber to become hard and brittle. These studies led to the analytical and synthetic uses of ozone. From 1904-1916 he was a professor at Kiel. Disenchanted with academic life, he became Director of Research for Siemens and Halske, the German company co-founded by the electrical pioneer, Werner von Siemens, his father-in-law. Not surprisingly, Siemens went into the business of producing ozone generators. The studies of Rudolf Criegee (1902-1975; Karlsruhe) produced a unified mechanism for the process of ozonolysis.
M. Rubin, Bull. Hist. Chem., 2001, 26, 40.
M. Rubin, Helv. Chem. Acta, 2003, 86, 930.
Reading Assignments:
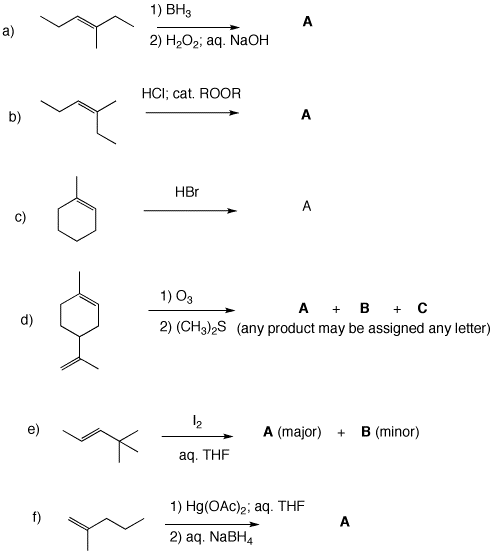
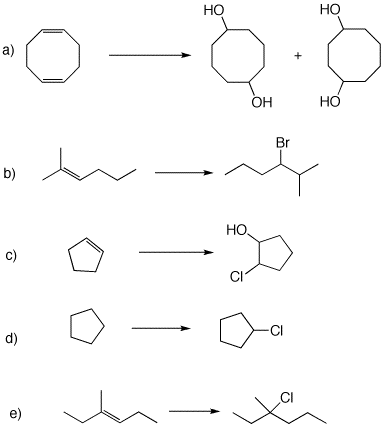
a)The alkane and alkene modules in ORGO will help with this Problem Set.. [Note that some of the problems in the alkene module deal with stereochemical issues. We will get there.]
b) Ozonolysis module.

Rudolf Criegee
(1904 - 1975)