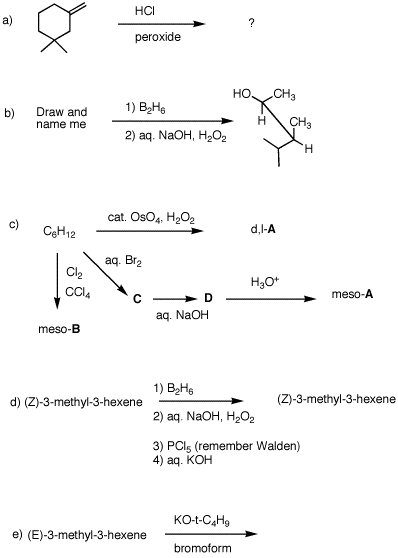
1. Reading assignments: b)
Ozonolysis
module. How do I approach solving problems
like #2-6? These problems require factual knowledge and
an ability to reason. Pretend you are a doctor and
patient has certain symptoms (the facts presented) and
you must call upon your knowledge to provide a diagnosis
(solution). Here
is a step-by-step analysis (diagnosis) of
#2
PS7 from F2000. Vladimir Vasilovich
Markovnikov (1838-1904)
a)The alkene module
in
ORGO.

|
2. Compound A is reduced with hydrogen to n-octane. Treatment of A with Br2/CCl4 produces (±)-B (C8H16Br2). Ozonolysis of A produces a single compound C. What are the structures A-C? Explain and illustrate. |
|
3. Nonane A undergoes free radical chlorination to produce two, and only two, monochlorides B and C. Treatment of B with aqueous sodium hydroxide affords D (C9H20O) and E. Under the same conditions, C gives rise to only E. A product of ozonolysis of E is aldehyde F (C8H16O). Treatment of E with H2SO4 provides G and G', both of which afford ketone H and 3-pentanone upon ozonolysis. G has a more negative heat of formation than G'. What are the structures of A-H? Explain and illustrate. |
|
4. Consider the diastereomer (2R*, 3S*)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane A. Show how you can prepare the corresponding alcohol, (2R*, 3R*)-3-methyl-2-pentanol, B from A without doing an SN2 displacement. |
|
5. Optically active compound A (C10H16) absorbs two equivalents of H2 to give optically active B. Ozonolysis of A provides a single compound C, (S)-2-methyl succindialdehyde (C5H8O2: see Table 20-3). |
|
6. Compound A (C13H20) liberates 54.5 kcal/mol of heat upon hydrogenation. Compound A undergoes ozonolysis; B is isolated. What are the structures of A and B? What two structures of B may be eliminated and why? [Use the heat of formation tables here and not the data in Table 7-1. The answers differ by a few tenths of a kilocalorie.] |
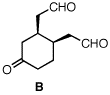 |
|
7. Provide solutions to each of the following problems. Pay attention to stereochemistry and mechanisms.
|