|
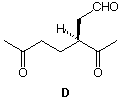
1. The alkene module in ORGO will give you a solid review of Chapter 7 and also introduce you to concepts covered in Chapter 8. You will see these examples again. You should also look at the ozonolysis module. 2. Compound A, C8H16, forms a meso compound B upon reaction with bromine in CCl4 and a d,l-diol C upon oxidation with OsO4. Ozonolysis of A provides a single ketone D. What are the structures of A-D? Show how they are formed. 3. Ozonolysis of A (C10H14O) affords only the ketodialdehyde B. What is the structure of A? Rule out other options. Explain.
 |
Vladimir Vasilovich Markovnikov (1838-1904) |
|
4. 1-Methylcyclohexene (A) reacts with HBr in the presence of peroxide to give a mixture of compounds B and C (C7H13Br). When compound B reacts with C2H5ONa/C2H5OH, compounds A and D are formed. Under the same reaction conditions, compound C only affords D. Compounds A and D provide the same product E (C7H14) upon catalytic hydrogenation. What are the structures of B-E? Explain how they are formed. |
|
5. An optically-active compound A (C10H16) reacts with H2 in the presence of Pt to afford B and C, both having the formula C10H20 and both optically inactive. A undergoes ozonolysis and reduction with (CH3)2S to give optically-active diketoaldehyde D and compound E. What are the structures of A, B, C, and E. Explain and illustrate. What is the R,S configuration of A? [Note: B and C are arbitrarily assigned. Here are some hints: What is the degree of unsaturation in A, B, and C? What is E -- do the math? How many ways can D be reassembled retrosynthetically to produce olefins that upon reduction give non-optically active compounds.] |
|
|
6. Compound A (C6H12) undergoes catalytic hydrogenation to provide B. Compound B forms four constitutional isomers upon free radical chlorination. Ozonolysis of A and reduction with (CH3)2S gives aldehyde C (not formaldehyde) and ketone D. Hydroboration of A gives a single compound E (C6H14O). What and how much can you conclude about the structures of A-E? Explain and illustrate. 7. Compound A forms only propionaldehyde B upon ozonolysis and reduction with (CH3)2S. Treatment of A with aqueous chlorine affords C (C6H13ClO). Exposure of C to aqueous NaOH produces racemate D (C6H12O). [Think about an intramolecular SN2 reaction (Williamson ether synthesis).] Compound D is also formed by the reaction of peracid with A. What are the structures of A-D? Illustrate and explain. 8. Compound A (C5H10) liberates 30 kcal/mol of heat upon hydrogenation (Chapter 7). Treatment of A with HCl in the presence of peroxide affords two compounds B and C both with the formula C5H11Cl. B is achiral and reacts readily with water to form D (C5H12O) while C is racemic and less reactive with water. What are the structures of A-D? Explain and illustrate. |