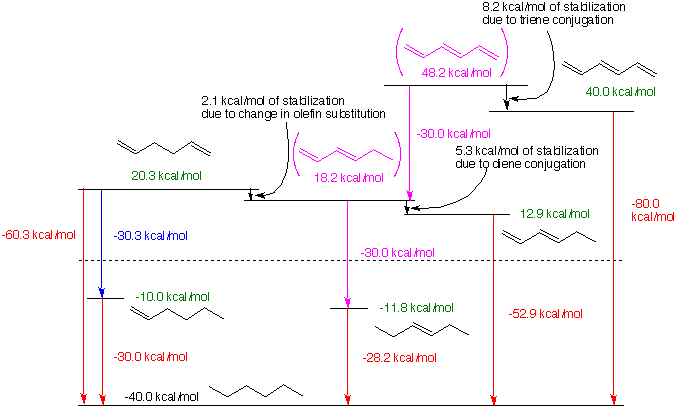
Estimates for the stabilization of conjugated dienes can be obtained from heats of hydrogenation (DHhydo).
The values used here were collected from the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) website. The values for the most recent heats of hydrogenation are used and the error of uncertainty has not been included. Consequently, calculated heats of formation (DHfo) may differ slightly from those in the Heats of Formation table. The heat of formation of n-hexane has been taken as DHfo=-40.0 kcal/mol from which the other heats of formation have been calculated. Code: Red - Reported heats of hydrogenation, Blue - Calculated heats of hydrogenation, Green - Calculated heats of formation, Magenta - Hypothetical compounds and reactions assuming no conjugation. For a separate window of the diagram, click here.

Starting on the left side of the diagram, the hydrogenation of 1,5-hexadiene to n-hexane liberates 60.3 kcal/mol of heat. Since hydrogenation of 1-hexene to n-hexane liberates 30.0 kcal/mol of heat, the calculated (DHhydo) of 1,5-hexadiene to 1-hexene is 30.3 kcal/mol. [The apparent discrepancy of 0.3 kcal/mol is within the error of measurement.] From the heats of hydrogenation and the heat of formation of n-hexane, the DHfo for 1,5-hexadiene and 1-hexene can be calculated. The DHfo of (E)-3-hexene is determined from the observed DHhydo , -28.2 kcal/mol. If the value for the DHhydo of 1-hexene is subtracted from the DHfo of (E)-3-hexene, the DHfo of (E)-1,3-hexadiene is determined to be 18.2 kcal/mol, a value that considers only the substitution pattern of the double bonds and no contribution from resonance. Given the observed DHhydo of (E)-1,3-hexadiene (-52.9 kcal/mol), the DHfo of the diene is calculated as 12.9 kcal/mol. The difference in energy between the DHfo of the hypothetical and real (E)-1,3-hexadiene (5.3 kcal/mol) gives the stabilization of the diene by conjugation through resonance. Similarly, the DHhydo of (E)-1,3,5-hexatriene is -80.0 kcal/mol. The difference in energy between this triene and its hypothetical model is 8.2 kcal/mol. The more conjugated double bonds, the more stability.