FINAL EXAM
Organic Chemistry
Chemistry 225b; 9 A.M., Friday, May 9, 2008
NAME (print): ______________________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_____________ Section Time:______________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Do problems first with which you are most comfortable. Important points and unknowns are in bold type. Do all preliminary work on the worksheets. The worksheets will not be graded. There are useful Tables on pages 15-17. The exam is 2 to 2-1/2 hours with an additional 1/2 hour for review. STOP writing when you are asked to do so. Put your name on the cover sheet and subsequent pages where indicated.
For question 2, do 1 of 3 choices.
For question 3, do 3 of 4.
For question 4, do 5 of 6.
For question 5, do 4 of 6.
For question 8, do 4 of 5.
.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage. If we canŐt read it; We canŐt grade it.
1. Structure/
Spectroscopy (30 pts) ________ 5. Kinetics/ (32 pts.) _________
Thermodynamics
2. Mechanisms (30 pts) _________ 6. Synthesis (30 pts.) _________
3. Reactions I (30 pts) _________ 7. Structure II (36 pts.) _________
4. Potpourri (30 pts) _________ 8. Reactions II (32 pts.) _________
______________________________________________________________________
Total (250 pts) ______________
1. (30 pts; 5 x 6 pts) Structure/Spectroscopy: The alkyl halide A, whose mass spectrum (Fig. 1) is shown below, forms a Grignard reagent B. When an excess of B reacts with aldehyde C, compound D is formed. The infrared (Fig. 2) and mass (Fig. 3) spectra of D are shown below.
Fig. 1

Fig. 2

Fig. 3
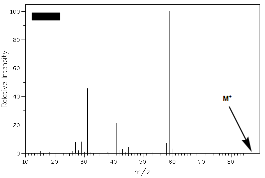
a) Explain briefly how Fig. 1 reveals the structure of A?
b) What is the significance of the absorption at ~3300 cm-1 in Fig. 2?
c) What is the molecular weight of D? Assume z=1 for m/z.
d) What is the structure of D? Explain briefly.
e) What is the structure of the ion that represents the base peak (intensity = 100) in Fig. 3?
2. (30 pts) Mechanism: Provide a mechanism (curved arrow formalism) for one of the following three reactions.

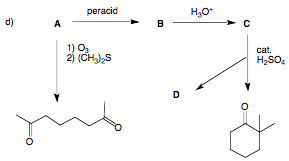
3. (30 pts; 3 x 10 pts) Reactions I: Provide the structures in three of the following four problems.
Pay attention to stereochemistry. If you do four problems, cross out the one you do not want graded.
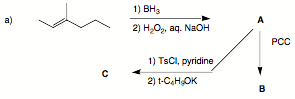
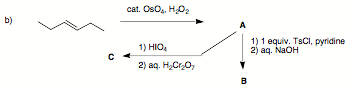

4. (30 pts; 5 x 6 pts) Potpourri: Complete five of the following six problems. If you do six problems, cross out the one you do not want graded..
a) N. Y. Times Crossword Puzzle, 41 Down. Clue: C4H8. (Monday, December 2, 2002)
![]()
b) The mass spectrum of dichloromethane, CH2Cl2, has molecular ions at M+ = 84, 86 and 88 with an intensity ratio of 9:6:1, respectively. See page 16. Explain the intensity ratio.
c) The structure of the optically inactive, racemic dibromide derived from the free radical bromination of (R)-1-bromo-2-methylpentane. Why is it optically inactive and racemic?
d) The structure and name of the cyclohexane, C8H16, whose two chair conformations are achiral and equal in energy.
e) A mixture of enantiomers (20% enantiomeric excess) has a rotation [a] = -24o. What is the rotation of the dextrorotatory enantiomer? Show work.
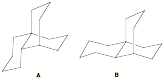
f) The difference in DHfo
(kcal/mol) of structures A and B is 0
kcal/mol. Explain.
5. (32 pts; 4 x 8 pts) Kinetics/Thermodynamics: Complete four of the following six problems.
If you do five or six problems, cross out the one(s) you do not want graded.
a) Of cis- and trans-3-hexene, the one with the greater heat of combustion. Explain briefly with a diagram.
b) The tosylate that undergoes an E2 faster in the presence of C2H5OH/C2H5ONa. Explain briefly.

c) The compound more likely to react via an SN2 or E2 reaction. Explain.
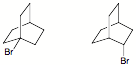
d) A nearly equal mixture of two monochloro compounds is anticipated in the free radical chlorination of 2,3-dimethylbutane. Explain and illustrate briefly. [relative rates: 1o = 1; 2o = 4.5; 3o = 5.5]
e) The difference in energy between the two chair conformations of cyclohexane 1 is 0.6 kcal/mol. Illustrate and show work. [Axial vs. equatorial for monosubstituted cyclohexanes: i-C3H7 = 2.1 kcal/mol; C2H5 = 1.9 kcal/mol; CH3 = 1.8 kcal/mol; gauche butane = 0.9 kcal/mol]
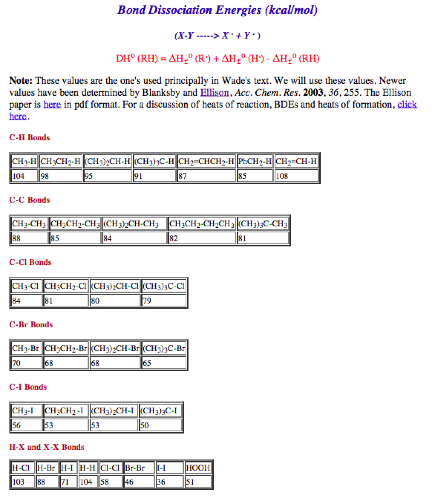
f) The heat of reaction in the monochlorination of
cyclohexane. See page 15. Show work.
6. (30 pts) Synthesis: A
student wishes to study the effect of hindered bases on E2 elimination
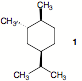
reactions. To this end, she requires the alcohol 1.
Because alcohol 1 is not
available commercially, she designs and executes a synthesis of 1 using only isobutylene (2-methyl-1-propene) and
formaldehyde as her only sources of carbon that find their way into 1. All
reagents and solvents were available to her, and to you, as you reconstruct the
synthetic plan that she may have used.

7. (36 pts) Structure II: Compound A, C7H14O, which has an infrared absorption at 1710 cm-1, reacts with methyl magnesium bromide to produce B, C8H18O. Compound B does not react with Cr (VI) reagents but it readily reacts with H2SO4 to form several compounds having the formula C8H16. One of these compounds C, gives D and E upon ozonolysis and dimethylsulfide reduction. Both D and E have the formula C4H8O, but D is oxidized to F (C4H8O2) with aqueous chromic acid while E is inert to these conditions. Compound F is not n-butyric acid. Compound C is measurably less exothermic than its geometrical isomer G upon catalytic hydrogenation. What are the structures A-F? [Hint: First, what are D and E? The infrared absorption is not essential but it is helpful.]
8. (32 pts; 4 x 8 pts) Reactions II: Do four of the following five problems by efficient pathways. If you do five, cross out the one you do not want graded.

Natural Abundance of Common Isotopes

Periodic Table
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets