Text: Wade, Organic Chemistry, 3rd
Edition.
FINAL EXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY 220
Tuesday, December 15, 1998
2:00 P.M.
NAME (print):
______________________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_________________ Section
Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Important points and
unknowns are in bold type. Do all preliminary work on the worksheets.
The worksheets will not be graded. There is a Periodic Table (page
16) and a BDE Table (page 17)
at the end of the exam. The exam is 2 to 2-1/2 hours with 1/2 hour
for review. STOP writing when you are asked to do so. Remember:
Neatness is to your advantage. Have a GREAT winter break! Best of
Luck in Chem. 221!
1. Potpourri I (30 pts) ______ 5. Mechanisms (20 pts) _______
2. Structure Proof (30 pts) ______ 6. Organic Reactions (40 pts)
_______
3. Synthesis (30 pts) ______ 7. Kinetics (28 pts) _______
4. Free Radicals (40 pts) ______ 8. Potpourri II (32 pts) _______
TOTAL: (250 pts) ___________
1. Potpourri I: (30 pts) Circle the best answer for each of the
following:
a) The strongest acid
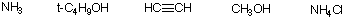
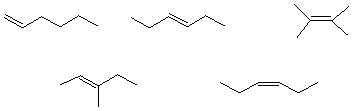
b) The hexene with the greatest heat of combustion
c) The closest value (kcal/mol) for DGo between the
chair conformations of trans-1,2-dimethylcyclohexane
1.8
0.9
0
2.7
indeterminate
d) The ratio of molecular ions in the mass spectrum of
1,2,3-tribromopropane
1:1:1
9:6:1
3:1
1:3:3:1
1:2:1
e) The bond with the lowest energy IR absorption
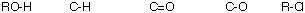
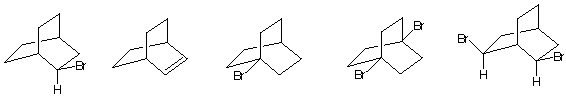
f) The compound with three singlets in its proton decoupled 13C
NMR spectrum
2. Structure Proof: (30 pts) An unknown compound A reacts with
catalytic OsO4 and stoichiometric
H2O2 to give a meso diol B. Ozonolysis and zinc
reduction of A affords a single compound C, whose 1H NMR spectrum is
the following : d 0.99 (3H, t, J = 7 Hz),
2.05 (3H, s) and 2.40 (2H, q, J = 7 Hz). Compound C displays 4
singlets in its proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum. One of
the singlets is of weak intensity and it is located at 207 ppm.
Compound C also displays a signal at 1710 cm-1 in its IR
spectrum and it has a molecular ion in its mass spectrum of m/z = 72.
What are the structures of A-C? Show how the data leads to your
answers.
A -----> _________________________
B -----> _________________________
C -----> _________________________
3. Synthesis: (30 pts) Design a synthesis of 3-methyl-3-pentanol
from (E)-2-butene as the only source of the carbon skeleton. All
necessary reagents are available to you.
[ Note that the product contains six carbons and the starting
material has four carbons.]
4. Free Radicals: (40 pts) Write the radical chain reaction for
the monochlorination of 2,2-dimethylpropane (neopentane)
[ORGO, Alkanes #1]. Provide
the initiation step, each of the propagation steps and the overall
reaction. Calculate the DHo for
each propagation step and the DHo for the overall reaction. Provide
an energy vs. reaction co-ordinate diagram for the reaction
designating the energies you have calculated. Do justice to the
Hammond Postulate. BDEs are on
page 17 (last page).
initiation step --->
1st propagation step --->
DHo = ____
2nd propagation step --->
DHo = ____
Overall reaction --->
DHo = ____
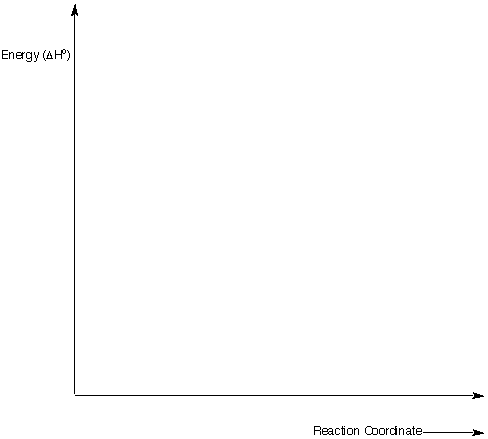
5. Mechanisms: (20 pts) Write a mechanism (curved arrows, charges,
etc.) for one of the three reactions shown below. Do not do more than
one!
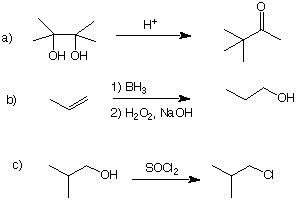
6. Organic Reactions: (40 pts) Draw the structure of the major
product in each of the following reactions. Pay attention to
stereochemistry.
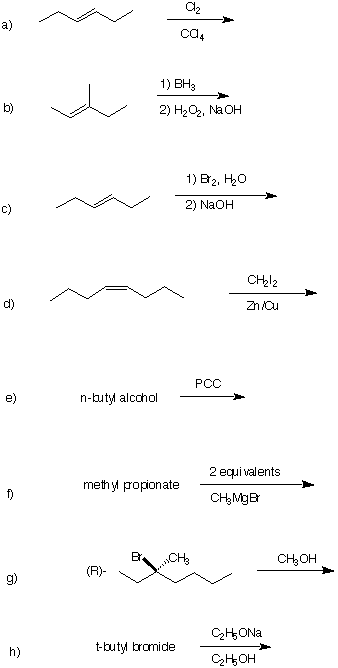
7. Kinetics: (28 pts) In each of the following examples, one of
the reactants reacts faster than the other one with the designated
reagent. Circle the faster reacting compound, draw the structure of
the product and, in as few words as possible, justify your answer.
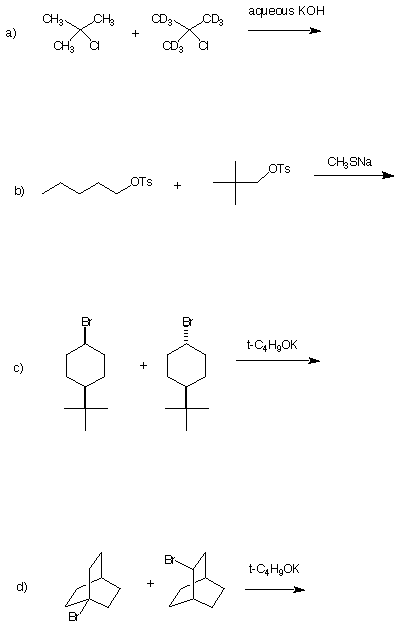
8. Potpourri II: (32 pts) A chemist requires a sample of
(S)-2-chlorobutane (6). She designs and executes the following
synthesis from (+)-ethyl lactate (1).
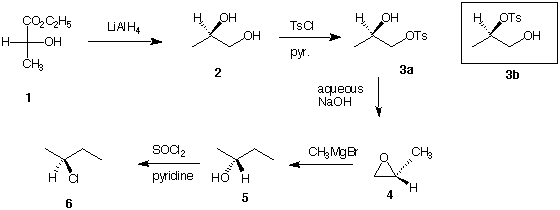
a) (8 pts) She chose not to form diol 2 by catalytic osmylation of
propene. Dihydroxylation with KMnO4, although inexpensive
relative to OsO4, was also rejected. Why?
b) (8 pts) The reaction of diol 2 with p-toluenesulfonyl
chloride/pyridine gave mostly monotosylate 3a and little monotosylate
3b. In her enthusiasm to proceed, she used a mixture of 3a and 3b to
form the chiral epoxide 4 by an intramolecular Williamson ether
synthesis, the optical purity of 4 was less than when 3a itself was
used in the reaction. Why was the optical purity of 4 diminished when
the mixture of 3a and 3b was used?
c) The enantiomerically-pure epoxide 4 was added to
CH3MgBr in ether. The unpurified products of the reaction
were reacted directly with thionyl chloride as described. Careful
distillation of the reaction products provided the desired alkyl
chloride (S)-6 and a small amount of an optically inactive isomer 7,
whose 1H NMR spectrum is shown below. [The proton
decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of 7 showed three singlets. Mass spectrum
molecular ion of 7: m/z = 92 and 94].
i) (8 pts) What is the structure of 7?
ii) (4 pts) How was isomer 7 formed?
iii) (4 pts) What are the relative intensities of m/z = 92 and 94
?
![]()

![]()





