NAME (print): ____________________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_______________ Section Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper. Do the questions with which you are most comfortable first.
The exam is 100 points . Important items are in bold.
You may do 4a or 4b. Mark the question you want graded in case you work on both of them.
In question 4a, you have a choice of one of three questions.
Do all preliminary drawing and computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded.
If you run out of space, write on the back of the preceding page.
The exam is 50 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. Analysis (20 pts) ______
2. Mostly Stereochemistry (20 pts) _____
3. Synthesis (20 pts) ______
4a. Mechanism I (20 pts) ______
(Choose one of three)
or
4b. Mechanism II (20 pts) ______
5. Potpourri (20 pts) ______
________________________________________
Total (100 pts)
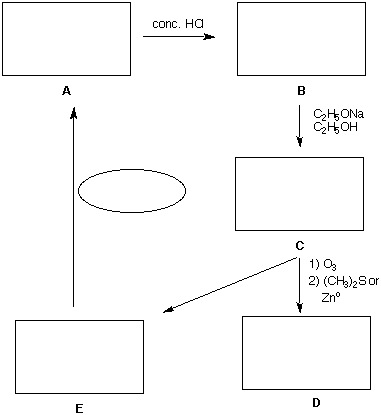
1. Analysis: (20 pts) An unknown compound A (C7H16O) reacts with sodium metal or a Grignard reagent to liberate H2. Compound A reacts readily with concentrated hydrochloric acid via an SN1 mechanism to form B (C7H15Cl). Compound B reacts with NaOC2H5 in ethanol by an E2 mechanism to form a single compound C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C followed by reduction with either dimethyl sulfide or zinc metal gives D (C2H4O) and 3-pentanone (E). Determine the structures of A-D and place them (A-E) in the appropriate boxes below. How can E be converted into A? Place the reagent in the oval. [Hint: 1) PS 6/7, #3; 2) Work backwards from E.]

2. Mostly Stereochemistry: (5 x 4 pts. = 20 pts.) In each of the following problems a product, reactant or reagent is missing.
Fill in the missing item(s). Be very careful about stereochemistry.

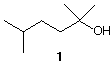
3. Synthesis: (20 pts.) A chemist needs to prepare 2,5-dimethyl-2-hexanol (1). Upon examining the structure of 1, she notices that the 8-carbon compound can be synthesized by forming the C3-C4 bond from two C4 compounds, both of which can be prepared from isobutylene (2-methylpropene). She obtains a cylinder of isobutylene (2-methylpropene) and converts some of it into compound 2 (C4H9Br) and some into compound 3 (C4H8O). After converting compound 2 into nucleophile 4, she reacts 4 with electrophile 3 and isolates the desired compound 1. Reconstruct her synthesis from isobutylene showing reagents. She had access (as do you) to all the reagents that would be necessary to conduct these experiments.
4a. Mechanism I: (20 pts.) Provide a mechanism and brief comments on one of the following topics. Grade this one (check here): ______
a) The mechanism of addition of HBr to 1-butene in the presence of peroxide.
b) The mechanism of anti-Markovnikov addition of water to 1-butene (i.e., hydroboration and oxidation).
c) Show how (E)-2-butene forms (2R,3S)-2,3-dibromobutane (i.e., meso) via a pair of enantiomeric bromonium ion intermediates. [Label the chirality of the carbons in the intermediate bromonium ion.]
4b. Mechanism II: (20 pts.) The Barbier-Wieland Reaction (1912) is a chemical degradation process of a carboxylic acid to its lower homologous acid. Thus, pentanoic acid, (by way of an ester derivative, such as methyl pentanoate 1) is converted from a C5 carboxylic acid to the lower homologous acid (C4) butanoic acid 3 as shown in the reaction sequence below. Grade this one (check here): ______
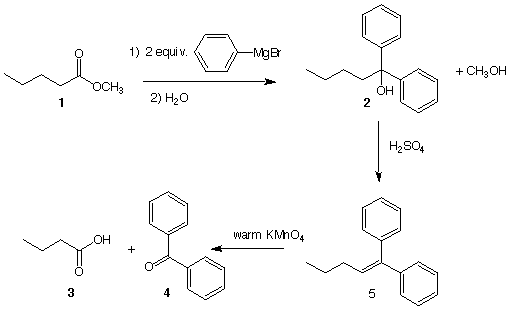
a) Why is phenyl magnesium bromide superior to methyl or ethyl magnesium
bromide? [Hint: Think about 2 ---> 5.
b) Write a mechanism for the reaction 1 --> 2?
4b. Continued:
c) Why is the olefin-forming step an E1 process? Illustrate and explain briefly.
d) How might aqueous NaOH be used to separate butanoic acid 3 (pKa = 4.3) from benzophenone 4, a non-acidic compound?
5. Potpourri: (5 x 4 pts. = 20 pts.) Circle the best answer(s) for each of the following.
a) The compound with the smallest rate constant for E2 elimination.
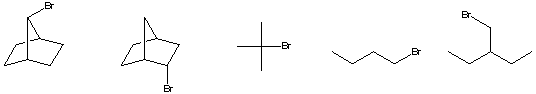
b) The alkene C5H10 with the greatest heat of combustion
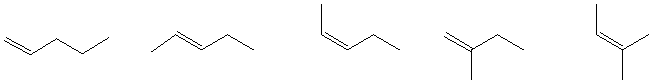
c) The greatest number of compounds at the same oxidation level.
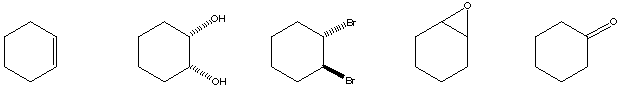
d) The compound with the different degree of unsaturation.
C6H10BrCl C8H17NO2 C17H34ClN3
e) The alcohol with the closest melting and boiling points.
n-butanol isobutanol sec-butanol n-pentanol tert-butanol