NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
The exam is 100 points . Important items are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing and computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded. If you run out of space, write on the back of the preceding page.
The exam is 50 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (22 pts) ______
2. (18 pts) ______
3. (12 pts) ______
4. (24 pts) ______
5. (24 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. (22 pts) The accepted reaction pathway for the overall free radical chain bromination of ethane is shown in equation 1. The first propagation step of equation 1 has DHo = +10 kcal/mol while the second propagation step has DHo = -22 kcal/mol. Alternatively, one might have imagined the reaction of ethane with bromine to give 2 moles of methyl bromide by a free radical chain bromination (eq. 2) with methyl bromide being formed in each of the propagation steps. However, this process does not occur.
C2H6 + Br2 ---> C2H5Br + HBr (eq. 1)
C2H6 + Br2---> 2 CH3Br (eq. 2)
a) (8 pts) Write the two propagation steps that sum to eq. 2. [Propagation step 1
employs a bromine atom generated in the initiation step.]
step 1 --->
step 2 --->
b) (10 pts) Compute (show work) the exo/endothermicity [DHo (kcal/mol)] of each propagation step and for the overall reaction of part (a). [BDEs are on page 3.]
step 1 --->
step 2 --->
reaction --->
c) (4 pts) Briefly explain why eq. 1 is favored over eq. 2.
BDEs
2. (3 x 6 pts = 18 pts) Complete each of the following as instructed.
a) Illustrate and briefly explain the Hammond Postulate with an energy vs. reaction coordinate diagram for an exothermic reaction.
b) A pure enantiomer of compound A has [a]D = -120o. What is the rotation of a sample of A that is prepared from equal amounts of (±)-A and pure (-)-A? Show work.
c) When tert-butyl chloride reacts with an excess of methanol, both isobutylene and tert-butylmethyl ether are formed. If sodium methoxide (1 equivalent based on tert-butyl chloride) is present in the reaction mixture, only isobutylene is formed. Explain these results in terms of substitution and elimination mechanisms.
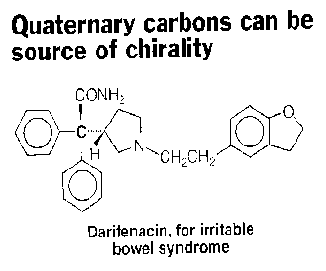
3. (3 x 4 pts = 12 pts) In the October 20, 1997 issue of Chemical & Engineering News in an annual article on chiral drugs, the claim shown below appeared. The quaternary carbon at issue is the one that is attached to the amide group (CONH2). In the original article, this carbon and its connecting bonds were highlighted in red to enforce the statement of the headline.
a) Circle the stereogenic carbon in Darifenacin and assign its R/S configuration.
b) Comment briefly on the headline about Darifenacin.
c) Having determined the R/S configuration, in a word, what can be concluded about the sign of the optical rotation of Darifenacin?

4. (4 x 6 pts = 24 pts) Predict the major product in each of the following reactions.
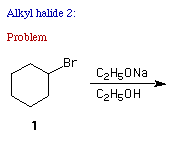
a) [See problem 2 in alkyl halides in ORGO.]
5. (24 pts) When (R)-1-chloro-2-methylbutane is chlorinated under free radical conditions, five dichloro constitutional (different structures) isomers can be formed.
a) (16 pts) Of these five, three will remain optically active and one of them can exist as a pair of configurational isomers (diastereomers). Draw these four structures below with relevant stereochemistry. Circle the two that are diastereomers and place their R/S designations adjacent to the relevant carbon atoms. You should have four structures.
b) (4 pts) Draw the structure of the one racemic dichloro compound. How did it become racemic?
c) (4 pts) Draw the structure of the one achiral dichloro compound. How did it become achiral?