FINAL EXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY 220
Friday, December 19, 1997
2:00 P.M.
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Important points and unknowns are in bold type.
Answer each question on the exam paper, except for questions 4 and 5 where you have a choice of
an a or b version. Be sure to check the one you want graded. Do all preliminary work
on the worksheets at the end of the exam. The worksheets will not be graded. There is a Periodic
Chart at the end of the exam. The exam is 2 to 2-1/2 hours with 1/2 hour for review. STOP
writing when you are asked to do so. REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage. Have a
GREAT winter break! Best of Luck in Chem. 221!
1. (48 pts) ______ 6. (24 pts) ______
2. (28 pts) ______ 7. (28 pts) ______
3. (30 pts) ______ 8. (28 pts) ______
4a or 4b. (25 pts) ______ 9. (14 pts) ______
5a or 5b. (25 pts) ______
____________________________________________________________________________
TOTAL: _________________
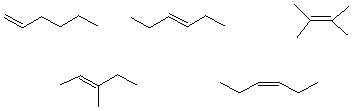
1. Potpourri: (8 x 6 pts = 48 pts) Circle the best answer or give the specific answer for
each of the following:
a) The strongest acid
![]()
b) The compound with the least negative heat of formation
c) The value (kcal/mol) for the equilibrium constant between the chair conformations
of trans-1,3-dimethylcyclohexane
1.8 0.9 0 1 indeterminate
d) The range (in ppm or d) of chemical shifts for a 13C NMR spectrum is how many
times greater than for a 1H NMR spectrum.
500 100 60 20 equal
e) The hybridization for one-third of the carbons in cyclohexene
sp3 s sp2 p sp
f) From the New York Times crossword puzzle (12/2/97, page E8);
70 Across. C4H8O2, e.g.
![]()
g) What is the specific rotation of a sample of (+)-limonene ([a]D +124o) that is
contaminated with 10% of its enantiomer? Show work.
h) Draw an energy diagram for the reaction
A --> B --> C. B is an intermediate.
The overall reaction is exothermic.
The second step is rate limiting.
2. Structure Proof: (4 x 7 pts = 28 pts) (S)-(+)-Limonene, (C10H16, [a]D +124o) is a
terpene found in the rind of lemons and oranges. Ozonolysis of (S)-(+)-limonene followed
by dimethyl sulfide or zinc reduction affords formaldehyde, CH2O, and compound 1.
Hydrogenation of limonene gives cis-and trans-1-isopropyl-4-methylcyclohexane.
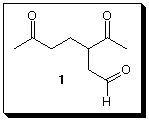
a) How many degrees of unsaturation are present in limonene?
b) What important information is gained from the hydrogenation experiment?
c) Draw (S)-(+)-limonene.
d) (S)-(+)-Limonene reacts with 2 equivalents of HCl in Markovnikov fashion to give
two optically inactive compounds C10H18Cl2. Draw their structures and
explain briefly.
3. NMR Spectroscopy: (5 x 6 pts =30 pts) An ester, C4H7O2Cl, has the 1H NMR spectrum
shown below. The downfield region integrates for 4 protons (overlap of signals) and the
upfield triplet (J=7 Hz) integrates for 3 protons.
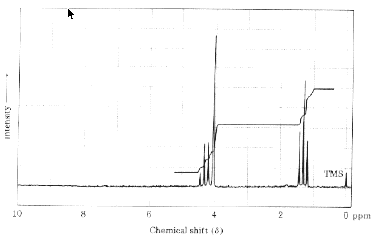
a) This spectrum appears to be recorded at 60 MHz rather than 500 MHz. How can
you tell?
b) Draw the spectrum as it would look at 500 MHz. [i.e., resolution of signals]
c) What is the relative ratio of the signals in the lowest field proton absorption (~d
4.2)?
d) How many singlets will appear in the proton decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of
the ester?
e) What is the structure of the ester?
4a. Synthesis: (25 pts) A dedicated, senior chemistry major, who is working on the weekend,
requires 2-hexanone (1, C6H12O) for an experiment. Because the stockroom is closed,
she cannot purchase the compound. However, she does discover a cylinder of propene
(C3H6) in the lab. Being well-versed in the chemistry of the fall term of Chem. 220, she
designs a synthesis of 1 using propene as the sole source of carbon. She has available
to her all necessary reagents. Devise a synthesis of 1 from propene that is consistent with
her thinking. [Hint: Locate the two C3 units present in 1. A friend of hers who took the
course last year had a similar dilemma.] Check here if you want 4a graded.---> __
4b. Synthesis: (25 pts) Disparlure (1) is the sex attractant of the female gypsy moth. It is an
optically active compound. Show how to synthesis racemic 1 from 1-dodecyne (C12H22),
and any other carbon compounds containing three or fewer carbons. All reagents are
available. Check here if you want 4b graded.---> __
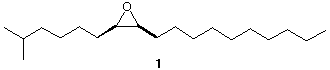
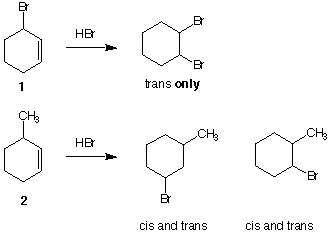
5a. Mechanism of Reaction: (25 pts) Consider the reaction of 3-bromo-1-cyclohexene (1) and
its analog 3-methyl-1-cyclohexene (2) with HBr as shown below. Explain why 1 gives
only one compound and 2 gives four compounds. [Hint: A knowledge of the mechanism
of the addition of bromine to alkenes will be helpful.] Check here if you want 5a
graded.---> __
5b. Mechanism of Reaction: (25 pts) Hydroboration/alkaline hydrogen peroxide oxidation is a
method for adding water across a double bond. In the case of 1-methyl-1-cyclohexene,
demonstrate your knowledge of this reaction. Consider the following issues:
regiochemistry (i.e, Markovnikov vs. anti-Markovnikov), stereochemistry of
hydroboration, and the mechanism of the oxidation of the C-B bond to a C-O bond using
the curved arrow formalism. Check here if you want 5b graded.---> __
6. Thermochemistry: (24 pts) For the reaction shown below, the following bond dissociation
energies (DHo) (kcal/mol) are available: CH3-H, 105; CH3CH2CH2-H, 101; (CH3)2CH-H, 98;
(CH3)3C-H, 96; HCl, 103; Cl2, 58; CH3CH2-Cl, 83; (CH3)2CH-Cl, 84. [Note: Use the bond
dissociation energies that best fit structures 1 and 3. Make bonds (downhill); break bonds
(uphill)].
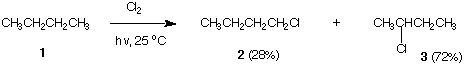
a) (8 pts) Calculate the relative reactivity of the two types of C-H bonds in butane. Show work.
b) (8 pts) Write the propagation steps (1 & 2) for the formation of 3.
c) (8 pts) Calculate the enthalpy for steps 1, 2 and for the overall reaction for the formation of 3.
Show work.
7. Reactions and Stereochemistry: (4 x 7 pts = 28 pts) Provide the information requested in each of
the following reactions. Pay attention to stereochemistry.
a) Major product? Is it optically active? Carbocationic or radical chain mechanism?
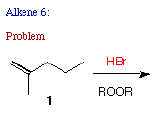
b) Major products 2 and 3? Show mechanism.

c) What is the structure of the product.? Is it optically active? Explain briefly.
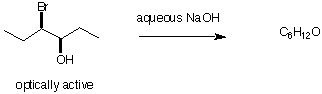
d) What is the reagent? Explain the results briefly.
(R)-3-bromo-3-methylhexane ---------------> d,l-3-methyl-3-hexanol
8. Kinetics: (4 x 7 pts = 28 pts) Complete each of the following questions as instructed.
a) Circle the compound that undergoes E2 elimination faster in the presence of potassium tert-
butoxide. Explain briefly.
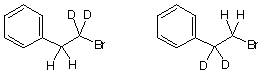
b) The major product formed when one equivalent of thiolate 1 and one equivalent of alkoxide
2 compete for one equivalent of methyl iodide. Explain briefly.
![]()
c) The compound that reacts faster with methanol: n-butyl bromide or tert-butyl bromide.
Explain briefly.
d) Does increasing the amount of solvent in an SN1 reaction increase the rate of the reaction?
Explain briefly.
9. (14 pts) The following message appeared on the Bulletinboard.
December 10:
Here is the take home, question for the final exam. Figure out the structure on the left in the correct absolute stereochemistry. Where have you seen it before? Have your answer ready for December
19. [ What is the structure on the cover of SHK?]
If you don't or didn't read the Bulletinboard, you may answer the following question for 7 pts.
Who developed Baeyer Strain Theory?
Worksheet
Worksheet
Worksheet
Worksheet