The material on last year's final is not unlike what you have seen in exams this term and in problem sets. Commentary is in red. The exam is a test of important factual information that has been stressed during the term as well as a test of your ability to apply knowledge and solve problems. FEZ
FINAL EXAMINATION
CHEMISTRY 220
Friday, December 20, 1996
2:00 P.M.
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Important points and unknowns are in bold type. Answer each question on the exam paper. Do all preliminary work on the blank sheets at the end of the exam. This section of the exam will not be graded. The exam is 2 to 2-1/2 hours with 1/2 hour for review. STOP writing when you are asked to do so. Remember: Neatness is to your advantage. Have a GREAT winter break! Good Luck in Chem. 221!
1. (30 pts) ______ 6. (25 pts) ______
2. (30 pts) ______ 7. (25 pts) ______
3. (40 pts) ______ 8. (25 pts) ______
4. (24 pts) ______ 9. (25 pts) ______
5. (25 pts) ______ Bonus: 1
______________________________
TOTAL: (250 pts) ______________
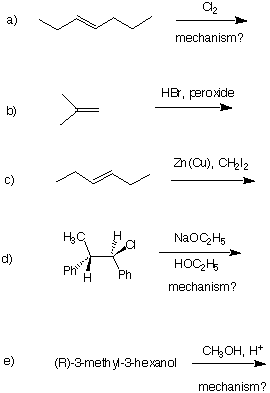
1. (5 x 6 pts = 30 pts) Provide the major product in each of the following reactions. For a), d) and e), provide a mechanism using curved arrows.

2. (5 x 6 pts = 30 pts) Provide the reagents (conditions) necessary to complete each of the following chemical transformations. Place your answer over the arrow. A maximum of two reactions is required to complete each transformation. Part e) was not covered.
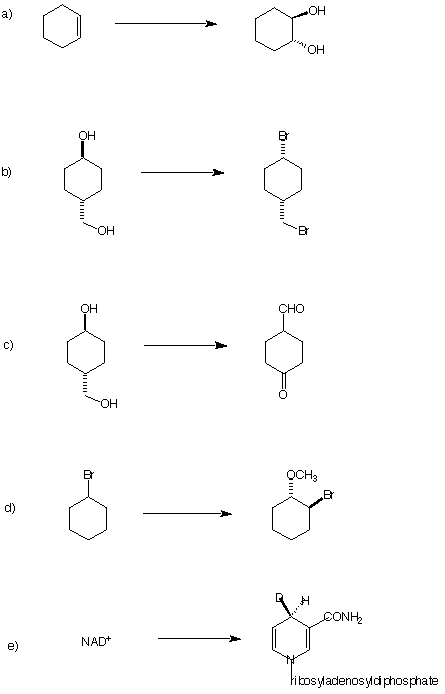
3. (8 x 5 pts = 40 pts) Circle the correct answer in each of the following:
a) The least acidic species.
C2H2 NH3 CH3COCH3 NH4Cl CH2=CH2
b) The compound with the shortest bond (bold):
![]()
c) The best estimate of the rotational barrier (kcal/mol) about the C-C bond in ethane.
0.9 -----3.0-------- 3.3---------3.9 ----------- 5.0
d) The hybridization of the carbons in acetylene.
s
p
sp
sp2
sp3
p
e) The heat of formation of n-pentane is DHfo = -35 kcal/mol. The best estimate for the heat of formation (kcal/mol) of n-heptane is:
-35
-40
-45
+45
+40
+35
f) A one hydrogen triplet appears in a 1H NMR spectrum with J = 6.0 Hz. The three peaks appear at d 0.9, 1.0, and 1.1. What is the frequency (MHz) of the spectrometer?
indeterminate
500
100
600
60
g) The value of DGo (kcal/mol) for the equilibrium between the two chair conformations of trans-1,4-dimethylcyclohexane (gauche butane interaction: 0.9 kcal/mol).
0
0.9
1.8
3.6
5.0
none of these
h) We didn't study Fischer projections in F97. but the "question" should sound familiar. "One of these things [Fischer projections] is not like the others. One of these things doesn't belong..."
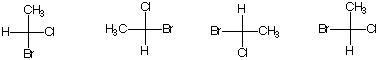
4. (4 x 6 pts = 24 pts) Answer each of the following questions.
a) Circle the compound that undergoes E2 elimination faster in the presence of a strong base. Provide a brief rationale.
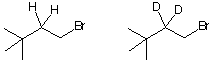
b) Circle the compound that forms an epoxide faster in the presence of base. Provide a brief rationale.
c) In the SN2 reaction shown below where [RBr] = 0.1 M and [R'S-] = 1.0 M, the rate of the reaction is not equal to k[RX][Nuc-] but rather k'[RX]. Explain.
CH3CH2CH2Br + CH3CH2S- ----------> CH3CH2CH2SCH2CH3
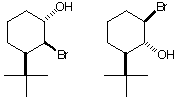
d) Circle the compound that reacts faster in an SN2 reaction with C2H5ONa. Provide a brief rationale.
![]()
5. (25 pts) An unknown compound A (C4H9Br) has the following 300 MHz 1H NMR spectrum. A blow-up of the spectrum is provided in the upper left-hand section of the spectrum. [The integrals above each of the four signals can be evaluated by inspection. The break in the integral for the signals at d1.7 and d1.8 is at the inflection point.] Sorry about the quality of the spectrum. The formula and 5b should give the answer away.
a) (20 pts) Draw the structure of A and assign chemical shifts to each of the hydrogen atoms.
b) (5 pts) Why do the two diastereotopic protons at d 1.8 appear as a simple pentuplet?
6. (25 pts) Consider the free radical reaction C2H6 + Br2 ---> C2H5Br + HBr, which is initiated by light. The bond dissociation energies (DHo) are: C2H5 H, 98 kcal/mol; Br2, 46 kcal/mol; C2H5-Br, 68 kcal/mol; HBr, 88 kcal/mol.
a) (10 pts) Write the two propagation steps in the reaction.
STEP 1 --->
STEP 2 --->
(b) (10 pts) What is the value of the endothermicity/exothermicity for each of the above steps? Show work.
STEP 1 --->
STEP 2 --->
(c) (5 pts) What is the value of DHo for the reaction? Show work.
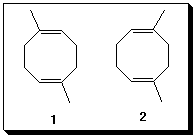
7. (25 pts) You have seen this one. The two compounds both have 5 singlets in their respective decoupled 13C NMR spectra. The spectra alone would make a structural assignment very difficult unless you had an authentic spectrum with which to compare. Thus, the question that follows: A difference of opinion between two of your classmates exists. He insists that the structures of the constitutional isomers 1 and 2 can be distinguished by 13C NMR spectroscopy because 2 has a plane of symmetry and 1 does not. He argues that the number of 13C NMR signals in the decoupled spectrum of each isomer should be different. She says he's wrong. She suggests a chemical procedure to distinguish between the two compounds. She points out that they learned two procedures (one procedure this year) for accomplishing this chemical transformation. She is correct. Briefly explain his faulty reasoning and one of her chemical solutions to the problem.
8. (25 pts) A dedicated, senior chemistry major, who is working on the weekend, requires 2,5-dimethyl-2-hexanol (1, C8H18O) for an experiment. Because the stockroom is closed, she cannot purchase the compound. However, she does discover a cylinder of isobutylene (C4H8, 2-methylpropene) in the lab. Being well-versed in the chemistry of the fall term of Chem. 220, she designs a synthesis of 1 using isobutylene as the sole source of carbon. She has available to her all necessary reagents. Devise a synthesis of 1 from isobutylene that is consistent with her thinking. [Hint: Locate the two C4 units present in 1].

9. (25 pts) An unknown compound A (C10H18O; [a]D25 = + 11.5o) reacts with O3 followed by dimethyl sulfide to provide B and C. Compound B displays a lone singlet at d 2.2 in its 1H NMR spectrum. The decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of B displays two singlets, one of which is at d 200 (200 ppm). Compound C (C7H12O2), which is optically active, can also be formed when (R)-4-methylcyclohexene D [the double bond is at C1 and C2] reacts with OsO4/H5IO6. Provide structures for A-D. Make sure you pay attention to the configuration of chiral centers. Account for NMR signals and the role of the reagents.