
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Do all preliminary drawing or computation in a blue book.
Blue books will not be collected.
The exam is 55 minutes.
The points should be an indication of the time required for solution.
STOP writing when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (15 pts) ______
2. (22 pts) ______
3. (20 pts) ______
4. (9 pts) ______
5. (15 pts) ______
6. (10 pts) ______
7. (9 pts) ______
________________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. (15 pts) A problem on conformational analysis.
a) (6 pts) Draw Newman projections of propane for the most and least stable
conformations. Label which one is which. In a single word, describe each diagram.
b) (5 pts) Draw a potential energy diagram (energy vs. angle of rotation) for rotation about a
C-C bond of propane.

c) (4 pts) Using the following values, calculate (show work) the barrier to rotation about a
C-C bond of propane: H/H, eclipsed, 1.0 kcal/mol; CH3/H eclipsed, 1.4 kcal/mol;
CH3/CH3, eclipsed, 2.5 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, gauche, 0.9 kcal/mol. Briefly explain
your reasoning. Locate this barrier in the diagram of part b.
2. (22 pts) On the structure of acrylonitrile.
a) (4 pts) Acrylonitrile (1) is used to make polymers. Redraw 1 using lines for bonds to
reflect the true geometry of acrylonitrile (be faithful to bond angles; ignore the
numbers). In a single word, how would best describe the shape of acrylonitrile (think
of the shapes of ethane, ethylene, and acetylene)?
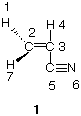
b) (6 pts) Rather than using lines for bonds, use an orbital (e. g., sp3, 1s, p) picture to
illustrate the structure of acrylonitrile. Label one of each hybrid orbital. Note: Only use
the large lobe of hybrid orbitals to make your picture clear.
c) (3 pts) How many s-bonds are in 1?
d) (3 pts) How many p-bonds are in 1?
e) (3 pts) What is the value (degrees) of the bond angle C3-C5-N6?
f) (3 pts) What is the value (degrees) of the dihedral angle H1-C2-C3-H4?
3. (20 pts) Tertiary-butyl alcohol 1 has a pKa of 18 while acetone 2, has a pKa of 20.
Answer the following questions regarding this equilibrium.
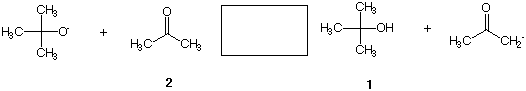
a) (3 pts) Circle the conjugate base of acetone.
b) (3 pts) What is the principal factor that makes the C-H bond of acetone about 1030
times more acidic than methane?
c) (3 pts) Place a square around the strongest acid.
d) (3 pts) Place equilibrium arrows in the rectangle to illustrate clearly the direction of
the equilibrium.
e) (3 pts) What is the value for Keq of the reaction shown?
Keq=
f) (5 pts) What is the value (show work) of DGoeq at 27 oC: R = 2.0 x 10-3 kcal/mol-
oK [DGo = -RT lnKeq]?
DGoeq=
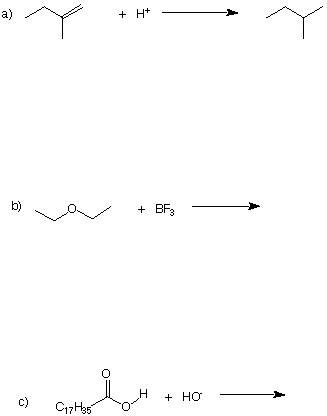
4. (a: 3 pts; b: 3 pts; c: 3 pts = 9 pts) All reactions must balance atoms and charges. Use
curved arrows for electron flow and complete or correct the following reactions by
supplying the missing information. Include charges where necessary.
5. (5 x 3 pts = 15 pts) Of ethylene, ethane, and acetylene, which one satisfies the following
criteria best.
a) The carbon-carbon bond with the lowest rotational barrier.
b) The largest C-H bond dissociation energy.
c) The shortest C-H bond.
d) The most acidic C-H bond.
e) A carbon-carbon bond length of 1.33Å.
6. (5 x 2 pts = 10 pts) In 1832, Liebig and Wöhler jointly published a paper on the benzoyl
radical, C7H5O. In those days, a radical was considered to be a group that could not be
altered. They prepared a number of derivatives of the benzoyl radical, changing the X
group in structure 1. For each of the following X groups, name the functional group that
is attached to the benzene ring (i. e.; RCOX).
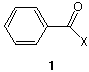
a) X=Cl
b) X=OR
c) X=NH2
d) X=R
e) X= RCO2 (attached at oxygen)
7. (3 x 3 pts =9 pts) Potpourri
a) Arrange the following in order of electron affinity: Methyl radical, fluorine atom, and
hydroxyl radical.
> >
b) Arrange the following in order of pKa: Cl3CCO2H, CH4, H2O, and CH3CO2H.
< < <
c) Arrange the following in order of boiling point: 2,2-dimethylpropane, n-pentane and
hexane.
< <