EXAM 2
CHEMISTRY 220
Friday, November 4, 2011
Answer Key
NAME (print): ________________________________________________________
TA:_________________ Sect. Day:_________________ Sect. Time:_____________
Fill in the information above. Place your name on the top right of subsequent pages.
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Record answers to questions on the exam paper.
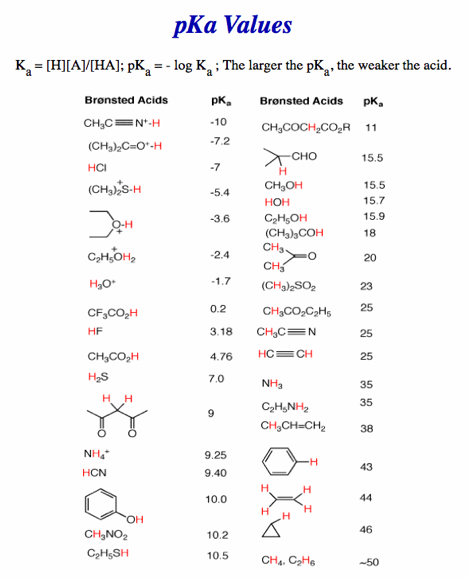
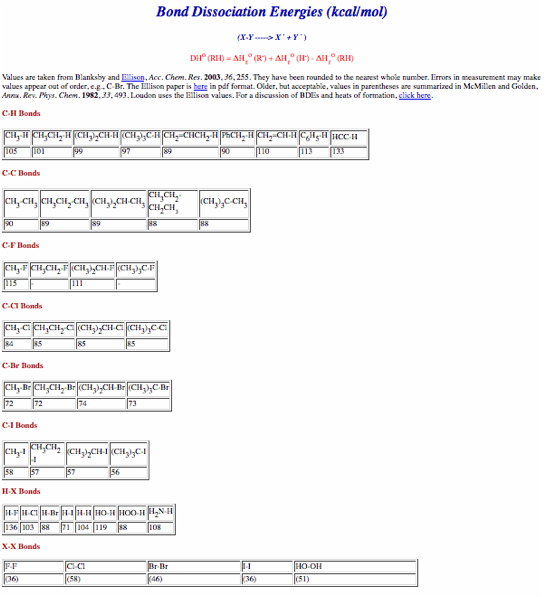
No calculators, electronic devices or earbuds. You may use molecular models. Important clues and structures are in bold. A Periodic Table (pg. 8), a pKa Table (pg. 9) and a Bond Dissociation Energy Table (pg. 10) are provided.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded. You may detach the work sheets from the exam.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (30 pts) Thermochemistry ______
2. (40 pts) Potpourri (do 4 of 6) ______
3. (30 pts) Conformation ______
4. (20 pts) Reactions (2 of 4) ______
______________________________________________
Total (120 pts)
Your grade above will be scaled to 100 points.
1. Thermochemistry: (30 pts.)
a) (20 pts.) Provide the two propagation steps for the free radical monochlorination of cyclooctane using the bond dissociation energies in the BDE Table (pg. 10). Place the reactants and products in the appropriate boxes and the BDEs on the lines. Calculate the heat of each propagation step and the heat of the overall reaction.
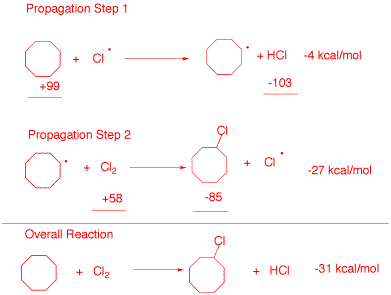
b) (10 pts.) Calculate the heat of formation of chlorocyclooctane. Data: DHfo (kcal/mol): cyclooctane, -29.7; HCl, -22.1.
heat of rxn = heat of
formation products - heat of formation of reactants
-31 = -22.1 + x -
(-29.7)
-31 = 7.6 + x
x = -38.6 kcal/mol
for heat of formation of chlorocyclooctane
2. Potpourri:
(40 pts., equal weight) Complete 4 of 6 of the following questions. You must complete a minimum
of two problems on this page (page 3).
If you do more than four
questions, cross out the ones that you do not want graded.
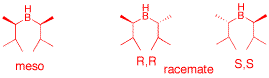
a) Two equivalents of 2-methyl-2-butene react with one equivalent of BH3 in a Markovnikov fashion to form two compounds of the general structure R2BH. One is a racemate and the other a meso compound. Provide stereochemical structures of the three stereoisomers. Identify them as a d,l pair or meso. Use their R,S-descriptors.
b) Provide an example of a stereospecific reaction. Explain briefly.
Each of two stereoisomers gives two
different stereoisomeric products when undergoing the same reaction. Z-2-butene
upon bromination gives a racemate; the E -isomer gives a meso compound. Mechanism
controlled reaction, anti addition.
c) (R, R)-tartaric acid ([a]D = +12o) is known as the “natural” enantiomer. What is the observed rotation of a solution containing four times as much (S,S)-enantiomer as the (R,R)-enantiomer? Show work.
(4-1)/(4+1) = 3/5 = 0.6 = op = ee
Major enantionmer pure is [-12].
-12 x 0.6 = -7.6 for the observed
rotation of the enantiomeric mixture.
…continued
d) Circle the compound(s) that are considered polar, aprotic solvents.
![]()
Correct answers: 1, 2, 5
Compounds 3 and 4 are both polar protic solvents.
e) The crown ether 18-C-6 is optimal for chelation of K+ while 12-C-4 chelates Li+ well. Draw a crown ether having Na+ chelated efficiently.
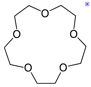
15-Crown-5, add a sodium cation to the center and chelate the
ion with each oxygen lone pair. Na
lies between Li and K on the periodic table. It is intermediate in size; requires intermediate sized
crown ether.
f) Circle the halides that will not form a stable Grignard reagent.
![]()
Answers:
1, 2, 5. Each one has an acidic
hydrogen that has a pKa less than R-H.
#1is the OH, #2 the N-H and #5 CO2H.
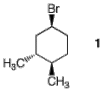
3. Conformation: (30 pts.) Consider the optically active stereoisomer of 1-bromo-3,4-dimethylcyclohexane (1) shown here.
a) (10 pts.) Label all centers of chirality with their appropriate R,S descriptors.
(1S, 3R,
4R) – 1-bromo-3,4-dimethylcyclohexane
b) (10 pts.) Draw the chair conformations of 1 below so that the equilibrium arrows are correct. Be sure all groups are clearly labeled axial or equatorial. Be sure you have the correct enantiomer.
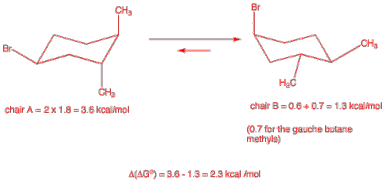
c) (10 pts.) Determine the value of D(DGo) for the above equilibrium given the following A- values for the monosubstituted (X) cyclohexane: X = Cl = 0.5 kcal/mol; X = Br = 0.6 kcal/mol; X = CH3 = 1.8 kcal/mol; X = C2H5 = 1.9 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3 gauche butane = 0.7 kcal/mol? Show calculations.
See above.
4. Reactions: (20 pts.) Identify the unknown structures and
answer questions in 2 of 4 of the
following problems. Explain
briefly. If you do three or four problems, cross out the one that you do not
want graded.
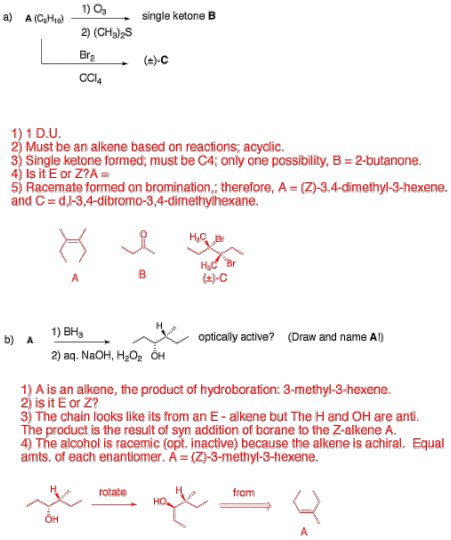
…continued
Periodic Table
Work Sheet
Work Sheet
Work Sheet