EXAM 1
CHEMISTRY 220
Friday, October 7, 2011
Answers
NAME (print): ________________________________________________________
TA:_________________ Sect. Day:_________________ Sect. Time:_____________
Fill in the information above. Place your name on the top right of subsequent pages.
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
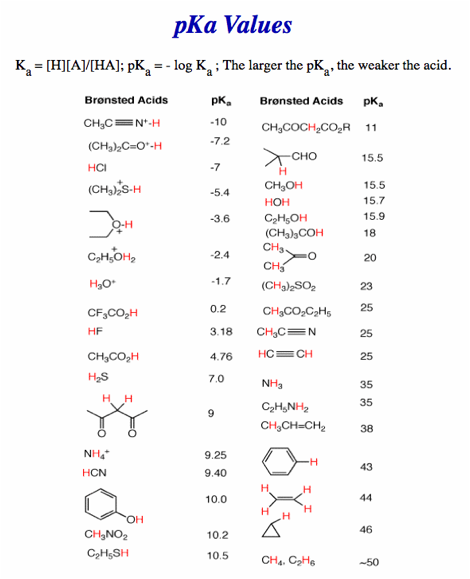
No calculators, electronic devices or earbuds. You may use molecular models. Important clues and structures are in bold. There is a Periodic Table on pg. 8 and a pKa Table on pg. 9.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded. You may detach the work sheets from the exam.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (20 pts) Conformation ______
2. (20 pts) Potpourri (4 of 5) ______
3. (20 pts) Thermochemistry, et al. ______
4. (20 pts) Bond Dissociation Energies ______
5. (20 pts) Concepts (3 of 4) ______
______________________________________________
Total (100 pts)
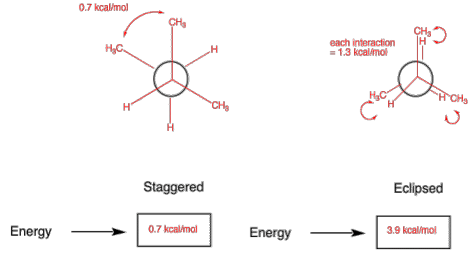
1. Conformation: (20 pts) For the eclipsed and staggered conformations of 2-methylbutane viewed along the C2-C3 sigma bond, draw a Newman projection of the most stable eclipsed and staggered conformations. Place the energies for each interaction in the Newman projections below. [Use the circles as templates for the Newman projections.] Calculate the total energy (kcal/mol) of both conformations. Place your answer in the appropriate box. [H/H, eclipsed, 1.0 kcal/mol; CH3/H eclipsed, 1.3 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, eclipsed, 3.6 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, gauche, 0.7 kcal/mol] Show your work!
2.
2. Potpourri: (20 pts.; equal weight) Circle the best
answer(s) where applicable in 4 of 5 of the following questions. If you do all five questions, cross out the
one that you do not want graded.
a) Sertraline (Zoloft), an antidepressant, has the molecular formula C17H17Cl2N. How many degrees of unsaturation does it have? Show work.
C17H17Cl2N ˆ C17H19N ˆ C18H20
Saturated C18 alkane = C18H38
38 – 20 = 18; 18/2 = 9 D. U.
b) Circle the compounds that are readily deprotonated by KNH2.[pKa NH3 = 35]
ethanol CH3CO2H
ethylene
NH4+
acetylene
pKaÕs 15.9 4.76 44 9.25 25
c) Circle the species with sp hybridized atoms.
HCN
ethylene
CS2
CH2=C=CH2
[BeCl3]-1
C & N C C2
d) Briefly explain and illustrate why ClHC=C=CHCl has a net dipole moment while
(E)-ClCH=CHCl does not.
1,3-dichloropropadiene has orthogonal
π-bonds owing to sp hybridization of C2. Thus the planes of H-C-Cl
angles are orthogonal. The two
C-Cl bonds are orthogonal. The compound is non-planar. Net dipole. The dichloro ethylene is planar with
all bond dipoles canceling.
e) Rank the following acids in order of decreasing pKa (high pKa to low pKa) with the numbers 1 – 5, respectively. [Least acidic carboxylic acid gets number 1.]
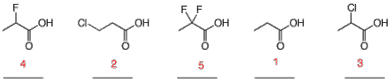
Non-halogenated acid least acidic.
Halogen adjacent to carbonyl acidifies more than halogen two carbons removed.
Fluorine more electronegative than chlorine. Two flourines better than one.
3. Thermodynamics, et al.: (20 pts.; equal weight)
a) a) Draw all six alkenes with the molecular formula C5H10.
![]()
b) Provide the IUPAC name for the most stable alkene in a). Explain briefly and illustrate how hyperconjugation stabilizes this compound. 2-methyl-2-butene. Sp3 C-H bonds donate electron density to the vacant, anti-bonding p-molecular orbital.
c) Provide the IUPAC name of the alkene in part a) that has the greatest heat of combustion.
1-pentene. [All six give the same amount of 5 CO2 and 5 H2O on combustion. The less substituted a double bond, the less stable (more positive heat of formation; less hyperconjugation)].
d)
Provide the IUPAC names of two alkenes in a) that have a difference of ΔHfo = ~1 kcal/mol. Which one is less stable? Why? (E)- and (Z)-2-pentene. (Z)-2-pentene is less stable due to non-bonding
van der WaalÕs interaction between cis methyl and ethyl.
e)
Given the following data (kcal/mol): n-pentane, ΔHfo
= -35.1; 1-butene,ΔHfo = 0. Determine the heat of hydrogenation
of the alkene in part c). The heat of formation of
1-pentene is 5 kcal/mol more negative than 1-butene, i.e., -5 kcal/mol. The heat of hydrogenation of 1-pentene
is -35.1 – (-5) = -30.1
kcal/mol.
4. Bond Dissociation Energies: (20 pts.) The heat of hydrogenation of (E)-3-hexene is given in the illustration shown below. Using bond dissociation energies (bonds made, bonds broken), determine the energy of the π-bond in the alkene. Show work. Typical BDEÕs (kcal/mol): CH3CH2-H, +101; (CH3) 2CH-H, +99; (CH3) 3C-H, +97; H2, +104.
![]()
heat of reaction equals bonds made (-) plus bonds broken (+).
Bonds made: 2 x (-99) kcal/mol = -198 kcal/mol[two secondary
C-H]
Bonds broken: H-H equals +104 kcal/mol; p-bond = x
Therefore:
-27 = -198 +104 +x;
x = -27 +198 -104
x = 67 kcal/mol for π-bond.
5. Concepts:
(20 pts.) Provide a brief explanation and illustration for 3 of 4 of the following concepts. If
you do all four questions, cross out the one that you do not want graded.
a) For the series of compounds 1) ethane, 2) ethylene and 3) acetylene, pKa decreases from 1 ˆ 3 while bond dissociation energy increases in the same order.
1) sp3 C-H; 2) sp2 C-H; 3) sp C-H. The greater % of s-character, the
closer the carbon holds electrons, the more labile the proton, i.e., more
acidic. BDE involves homolysis of the C-H bond. While the greater amount of
s-character allows for proton loss, it inhibits the loss of an electron because
they are held more tightly the greater the s-character..
b) The Hammond Postulate
Exothermic reaction, early transition state;
endothermic transition state, late transition state.
Écontinued
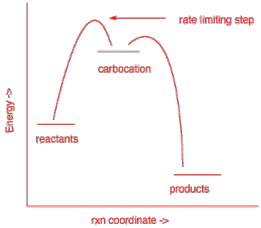
c) The rate limiting step in an exothermic reaction having an intermediate carbocation.
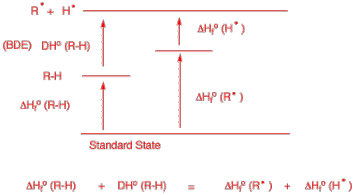
d) For the alkane R-H, the relationship between bond dissociation energy and the heats of formation of R-H, the R radical and the hydrogen atom.
Periodic Table
Work Sheet
Work Sheet
Work Sheet