EXAM 2
CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, October 14, 2005
NAME (print): _________________________________________ Your ID#: ___________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_________________ Section Time:__________
No Calculators! Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues and structures are in bold.
BDE Table, pg. 13; Heats of Formation Table, pg. 14.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (25 pts) Thermochemistry ______
2. (25 pts) Unknown Compounds ______
3. (25 pts) Potpourri ______
4. (25 pts) Reactions ______
___________________________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. (25 pts) Thermochemistry: A chemist wishes to assess the viability of preparing ethyl iodide from ethane in the presence of gaseous I2 at 298 oC.
a) (10 pts) Illustrate the initiation and propagation steps for this reaction. Using BDEs (see attached sheet), determine DHo for the four steps below. Place reactants and products in the squares and numerical values on the lines.
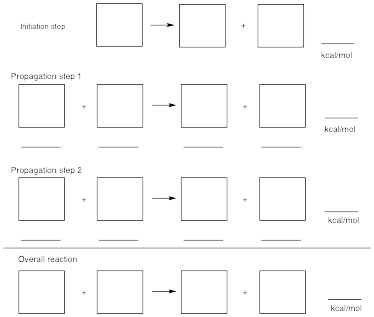
b) (5 pts) Determine the heat of sublimation of solid I2 at 298 oK using the heats of formation tables provided (see attached tables) and the answer to a). Show work.
c) (5 pts) Provide an Energy vs. Reaction Coordinate diagram for this reaction. Label the appropriate energies from part a). Be sure your diagram illustrates early and late transition states Hammond Postulate).

d) (5 pts) Is this process a good preparative reaction? Explain.
2. (25 pts) Unknown
Structures: Compound A (C6H14; what are the
possibilities?) undergoes free radical bromination to form principally
(>90%) monobromide B. When the free radical chlorination of A is conducted, five monochloro constitutional
isomers are formed. Compound B
is immiscible in water, forming two layers. However, when the test tube is shaken, heat is liberated and
the sample now appears homogeneous, forming compound C. If
compound B is treated with
aqueous NaOH, no C is formed,
but D (major) and E (minor) are produced.
a) (15 pts) What are the structures A-E?
Explain and illustrate.
Continued
on the next page………..
b)
(10 pts) Draw the structures of the monochlorides in the first column. Place an “X” in the boxes that apply to
each structure, i.e.; achiral, racemic, and/or optically active.
|
Monochloride |
Achiral |
Racemic |
Optically Active |
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. (25 pts) Potpourri:
Answer 4 of 5 of the
following questions. If you do five questions, cross out the one that you do
not want graded.
a) Bicyclo[2.2.1]heptane (1) is achiral and not meso while the dichloride 2 is both achiral and meso. Explain.
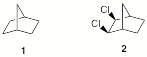
b) The number of possible stereoisomers of
A and B is given in parentheses. Explain only one of the examples. Pay attention to stereocenters and atropisomerism.
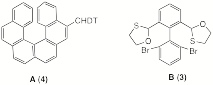
Continued on the next page….
c) A mixture of enantiomers has an optical
purity of 70% and an observed specific rotation [a]D
= -84o. What is the
specific rotation of the minor enantiomer and what percentage is it of the
mixture? Show work.
d) Upon free radical
chlorination, (R)-2-chlorobutane
forms -- among other dichlorides – dichloride 1 (optically inactive) and its stereoisomer 2 (optically active). If the ratio 1/2 = 4, what is the expected ratio when racemic 2-chlorobutane undergoes
the reaction? Name the dichlorides
1 and 2.
e) A 0.1M solution of an
enantiomer has [a]D +120o. What is the value of [a]D when the concentration of the solution is halved? Explain.
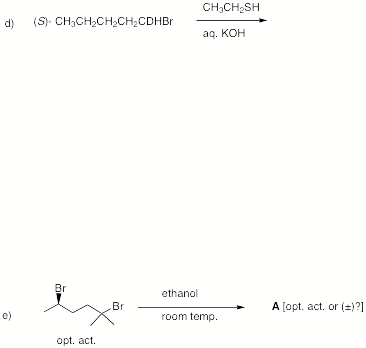
4. (25 pts) Reactions:
Provide the product in 4 of 5 of the following reactions.
Provide a brief explanation.
If you do five questions, cross out the one that you do not want graded.
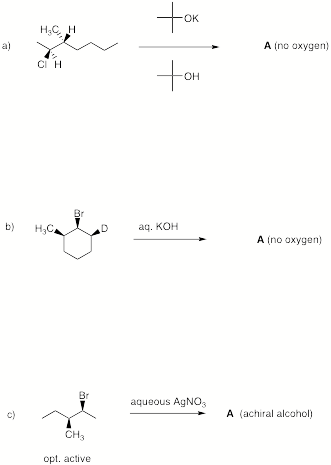
Continued on the next
page…….
4. Continued…
BDEs
http://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids/thermo/BDE.html
Heats of Formation
http://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids/thermo/heats-formation.html