EXAM 4
CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, December 6, 2002
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues, points, and structures are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded
There is a Periodic Table on the last page of the exam.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. Synthesis (20 pts) ______
2. Reactions (30 pts) ______
3. Structure (20 pts) ______
4. Potpourri (30 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. (20 pts) Synthesis: A chemist requires a sample 3-methyl-3-heptanol (1). She designs and executes a synthesis of 1 using 1-butene as her sole source of carbon atoms. She has access to all other reagents.
a) (15 pts) Show how you would accomplish this synthesis.
b)
(5 pts) Is compound 1 from the synthesis optically active or not? Explain
briefly.
2. (30 pts) Reactions: Provide the expected product(s) of the following
reactions. Pay attention
to stereochemistry.
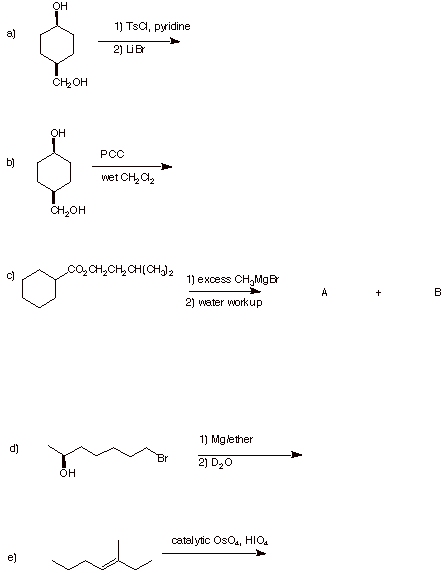
3. (20 pts) Structure: Given the reactions shown below,
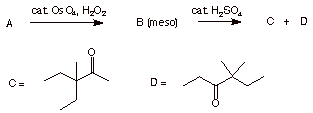
a) (10 pts) What are the structures of A and B? Explain and illustrate.
b) (10 pts) Show how C and D are formed from B.
4. (30 pts) Potpourri: Provide answers for the following questions. Circle your answers in all but #2.
|
a) How many stereoisomers of the tetramer of acetaldehyde (1) are possible? |
|
b) The remaining steps needed to convert alkene 1 into its geometrical isomer 2.
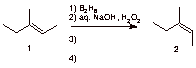
c) Functional groups that are unreactive toward a Grignard reagent
RCOOH ROH ester alkene ether
d) The major by-product in the oxidation of a primary alcohol to an aldehyde with PCC
under anhydrous conditions
ester carboxylic acid ether ketone amide
e) The compound not at the same oxidation level as the other four
![]()
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Periodic Table
