EXAM 2
CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, October 18, 2002
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues, points, and structures are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded
There is a Periodic Table on page 10 and a Bond Dissociation Energy Table on page 11.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (34 pts) ______
2. (16 pts) ______
3. (25 pts) ______
4. (25 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. Radical Chain Reactions (40 pts. total)
a) (10 pts) Provide the propagation steps and overall reaction for the major monochlorination product in the free radical chlorination of isobutane (2-methylpropane). Place the alkane in the first box on the left. Place the other reactants and products in the remaining boxes with their BDEs on the appropriate lines. (relative rates: k(1o) = 1; k(2o) = 4.5; k(3 o) = 5.5)

b) (6 pts.) Calculate the heat of reaction for each propagation step and for the overall reaction. Place your answers over ‘kcal/mol’ above.
c) (8 pts.) Calculate the heat of formation (DHfo) for the alkyl halide given the following data: DHfo (kcal/mol): n-butane, -30; isobutane, -32; HCl, -22; HBr, -9. Show work.
d) (10 pts.) Provide an energy profile of the reaction that does justice to the Hammond Postulate. Locate the heat liberated in each propagation step and in the overall reaction.

2. (16 pts.) The terpene carvone exists in nature as the separate enantiomers A and B. (R)-(-)-carvone smells like spearmint while (S)-(+)-carvone has the fragrance of caraway (dill) seeds.
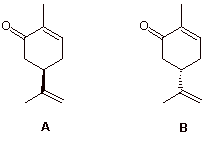
a) (5 pts.) Place the correct Cahn-Ingold-Prelog (CIP) configuration at the chiral center in A and B above.
b) (11 pts.) The optical rotation ([a]D) of pure laevorotatory carvone is 62.5o. A student needs 5.0 mL of this enantiomer for an experiment. S/he only has 4.5 mL so s/he unwittingly makes up the difference in volume with the other enantiomer. What is the optical rotation of the final mixture? Show work.
3. (25 pts, equal weight) Potpourri: Circle the best answer(s) in a-e.
a) The difference in the heat of formation of two isomers is equal to their difference in
heat of combustion heat of vaporization bond dissociation energy
enthalpy strain energy
b) “One of these things is not like the other. One of these things doesn’t belong.”
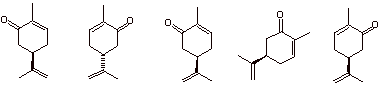
c) Terms associated with an E2 elimination
k[RX] intermediate deuterium isotope effect
inversion of stereochemistry stereospecific
d) The product of solvolysis of (S)-3-bromo-3-methylhexane in excess methanol
e) Draw a Fischer projection of (R,R)-tartaric acid [HO2CCH(OH)CH(OH)CO2H]
4. (25 pts.) Provide the expected products in each of the following reactions. Give a very brief rationale. Pay attention to stereochemistry.
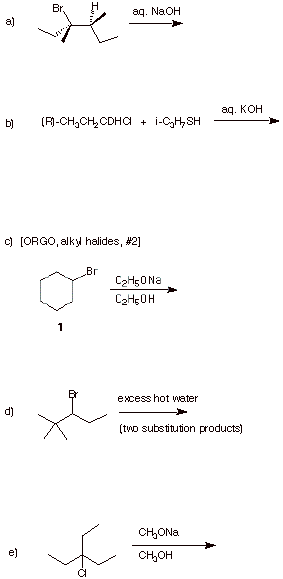
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Periodic
Table
BDE Table