EXAM 1
CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, September 27, 2002
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues and structures are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The work sheets will not be graded. There is a Periodic Table on the last page of the exam.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
Remember: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (24 pts) ______
2. (20 pts) ______
3. (25 pts) ______
4. (16 pts) ______
5. (15 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
1. (24 pts; equal weight) Compound A (C10H20), which is a 1,4-disubstituted cyclohexane, has DG0 = 0 kcal/mol for the difference in energy between its two chair conformations. [DGo (kcal/mol) values for axial and equatorial substituents in mono-substituted cyclohexanes: -CN, 0.2; -COOH, 1.4; -CH3, 1.7; -CH2CH3, 1.8; -CH(CH3) 2, 2.1; -C(CH3)3, 5.4.]
a) Name alkane A.
b) Draw the structure of alkane A in each of the templates shown below. Be clear about equatorial and axial bonds where applicable.

c) Draw the chair conformations of the stereoisomer of compound A in each of the appropriate templates shown below. Be clear about equatorial and axial bonds and pay attention to the arrows.
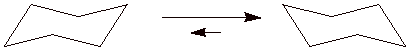
d) What is the difference in energy between the two chair conformations of this stereoisomer? Explain briefly.
2. (20 pts) For the eclipsed and staggered conformations of 2-methylpentane viewed along the C2-C3 sigma bond, draw a Newman projection of the most stable eclipsed and least stable staggered conformations. Place the appropriate energies in the Newman projections below. [Use the circles as templates for the Newman projections.] Calculate the energy (kcal/mol) of both conformations. Place your answer in the appropriate box. Show work. [H/H, eclipsed, 1.0 kcal/mol; CH3/H eclipsed, 1.3 kcal/mol; C2H5/H, eclipsed, 1.4 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, eclipsed, 3.0 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, gauche, 0.9 kcal/mol; CH3/C2H5, gauche, 1.0 kcal/mol.]

3. (25 pts.; equal weight) Circle the best answer(s) in each of the following:
a) The C1-C4 dihedral angle in the most stable conformation of n-butane.
0 30 60 120 180
b) The compound C8H18 expected to have the fewest number of degrees between its melting and boiling points.
n-octane 2,2,3,3-tetramethylbutane 2,2-dimethylhexane
2,3-dimethylhexane 2,3,4-trimethylpentane
c) The acids that are readily deprotonated by NaOH
Cyclohexane HCN NH3 NH4+ CH3CO2H
d) Species with sp3 hybridization
NH4+ ethylene BF4- ethane BeH2
e) Compounds with net dipole moments
BrCH2CH2Br CH2Br2 trans- BrCH=CHBr CBr4 HCBr3
4. (16 pts.) The concept of resonance plays an important role in organic chemistry. Explain and illustrate the role of resonance in one of the following cases:
a) The relative acidity of methanol vs. acetic acid
b) The enhanced ability of CH2=CHCH2Br to ionize to R+ Br-
c) Stabilization of the carbocation RCHOCH3
5. (15 pts) Provide a molecular orbital representation of one of the following compounds. Include pi-bonds, p-orbitals, etc. Provide necessary commentary.
a) allene (1,2-propadiene) CH2=C=CH2
b)
methylacetylene (1-propyne) CH3CCH
Work Sheets
Work
Sheets
Work
Sheets
Periodic
Table