CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, October 19, 2001
NAME (print): ______________________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_________________ Section Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues and structures are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The
work sheets will not be graded. There is a Periodic Table on page 11 of the exam.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (40 pts) ______
2. (25 pts) ______
3. (20 pts) _____
4. (20 pts) ______
___________________________
Total (105 pts)
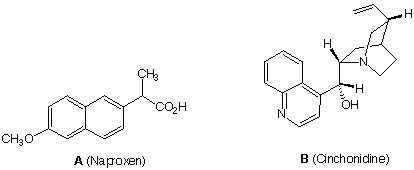
1. (8 x 5 pts = 40 pts) Naproxen A ([a]D = +65o) is an analgesic that is sold by
prescription. Its sodium salt is the active ingredient in the over-the-counter product,
Alleve. It is the (S)-(+)-enantiomer of Naproxen that is active and it is sold as such.

a) Is the phrase "(S)-(+)- enantiomer" redundant? Why or why not?
b) Draw the dextrorotatory enantiomer of Naproxen using the template below.
The original method for preparing (S)-(+)-Naproxen was to accomplish a large scale
resolution of (±)-Naproxen with the naturally occurring base, cinchonidine B ([a]D = -110o).
c) Describe briefly, in general terms, using the letters A (Naproxen) and B
(Cinchonidine) and the signs of rotation, the principle behind the resolution.d) Which salt is more likely to be less soluble, seeing that cinchonidine got the job
done?
e) Circle the chiral centers in cinchonidine.
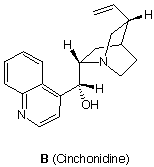
e) Label half [your choice] of the chiral centers with their R/S configurations. Use the
structure below.
f) On a bad day, the rotation of a sample of Naproxen obtained by resolution was
+39o. What percentage of each enantiomer was present and what was theenantiomeric excess of the sample? Show work.
g) Why is resolution generally a relatively expensive way of preparing pure (S)-(+)-Naproxen? Be brief [Hint: Think about the % yield of the reaction.]
2. (25 pts) Consider the free radical chlorination of cyclopentane.
a) ( 4 pts.) What is the initiation step?
b) ( 7 pts.) Provide the two propagation steps and the overall reaction for this process.
Place the reactants and products in the appropriate boxes. Cyclopentane goes in
the first box.

c) ( 7 pts.) Determine the bond dissociation energy (DHo) of a C-H bond in cyclopentane
using the data on the last page (pg. 12) of the exam. Place the data on the lines under
the appropriate boxes and at the end of each reaction that requires a
value. Show any calculations below.
d) ( 7 pts.) Using Hess's Law [DHo (rxn) = DHo (products) - DHo (reactants)] and the
heat of the overall reaction, determine the heat of formation of chlorocyclopentane
given: DHfo (cyclopentane) = -18 kcal/mol; DHfo (HCl) = -22 kcal/mol. Show
work.
3. (4 x 5 pts. = 20 pts.) Provide the major product expected in each of the following
reactions and the mechanism of formation: SN2, E2, SN1, or E1. Pay attention to
stereochemistry and optical activity.

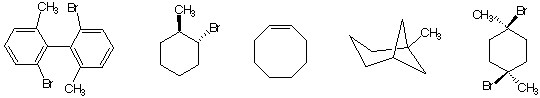
4. (4 x 5 pts. = 20 pts.) Circle the best answer(s) in each of the following questions.
a) Which of the compounds (1-4) in the Walden cycle are of the (S)-configuration?

b) Which of the following compounds are capable of existing as enantiomers?
c) In calculating [a]D = aobs/c . l, the value of "l" is measured in
|
|
|
|
|
|
d) The alkyl bromide that undergoes SN2 reaction the fastest
|
CH3-H |
CH3CH2-H |
(CH3)2CH-H |
(CH3)3C-H |
CH2=CHCH2-H |
PhCH2-H |
CH2=CH-H |
|
CH3-CH3 |
CH3CH2-CH3 |
(CH3)2CH-CH3 |
CH3CH2-CH2CH3 |
(CH3)3C-CH3 |
|
88 |
85 |
84 |
82 |
81 |
|
CH3-Cl |
CH3CH2-Cl |
(CH3)2CH-Cl |
(CH3)3C-Cl |
|
84 |
81 |
80 |
79 |
|
CH3-Br |
CH3CH2-Br |
(CH3)2CH-Br |
(CH3)3C-Br |
|
70 |
68 |
68 |
65 |
|
CH3-I |
CH3CH2 -I |
(CH3)2CH-I |
(CH3)3C-I |
|
56 |
53 |
53 |
50 |
H-X and X-X Bonds
|
H-Cl |
H-Br |
H-I |
H-H |
Cl-Cl |
Br-Br |
I-I |
|
103 |
88 |
71 |
104 |
58 |
46 |
36 |