CHEMISTRY 220a
Wednesday, December 12, 2001
NAME (print): ______________________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Section Day:_________________ Section Time:__________
The exam is 55 minutes and it covers the semester's work.
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important clues and instructions are in bold.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The
work sheets will not be graded. There is a Periodic Table on the last page of the exam.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (20 pts) ______
2. (20 pts) ______
3. (20 pts) ______
4. (20 pts) ______
5. (20 pts) ______
______________________________
Total (100 pts)
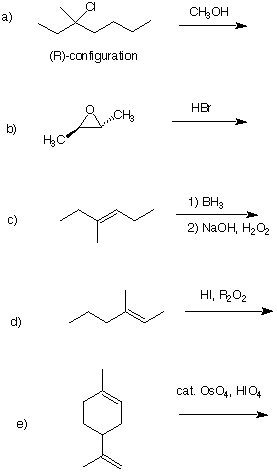
1. (5 x 4 pts. = 20 pts.) Provide the expected product(s) of each of the following reactions.
Pay attention to stereochemistry.

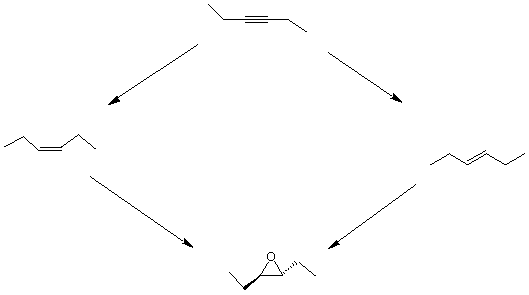
2. (20 pts.) Provide the reaction conditions necessary to convert 3-hexyne into the trans-
epoxide shown below. Place the reagents next to the the four arrows. Some
transformations may require more than one step.
3. (4 x 5 pts. = 20 pts.) Complete each of the following questions.
a) A solution of a 60/40 mixture of the two enantiomers of a compound is prepared. The
observed optical rotation is +80o. What is the optical rotation of the levorotatory
enantiomer? Show work.
b) An overall chemical reaction having an intermediate is exothermic by 20 kcal/mol and
the first step is endothermic by 3 kcal/mol. The second step has an activation energy (Ea) of 1 kcal/mol. What is the rate limiting step in the reaction? What is DHo for the second step? Illustrate with an energy diagram.
c) What is the major free radical monochlorination product of n-butane? Show caculations.
d) List the following compounds from left to right in increasing order of pKa: H3O+,
CH3CO2H, H2O, (CH3)3COH, HCCH, NH3, CH4.
4. (20 pts.) Design a synthesis of 3-ethyl-2-pentene (C7H14) from ethylene as your source of
carbon atoms. All reagents are available to you. [Note: Ethylene has an even number of
carbons; C7H14 has an odd number.]
5. (20 pts.) Compound A, C8H12, reacts with hydrogen in the presence of the catalyst Pt to
afford B, C8H14. Compound B forms only 2 monobromination derivatives, C and D,
upon free radical bromination. Compound C forms A and alcohol E (C8H14O) upon
reaction with KOH. Compound D cannot undergo an SN2 reaction (why?) with KOH nor
can it undergo elimination. What are the structures of A-E? Show your reasoning. [Hint:
This problem should be familiar to you.]