
CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, November 10, 2000
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Write your name on the top of each page where indicated.
Important items are in bold.
A Periodic Table is on page 10.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets (pgs. 7-9). The work sheets
will not be graded.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (20 pts) ______
2. (20 pts) ______
3. (20 pts) ______
4. (20 pts) ____
5. (20 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
1) (20 pts.) Optically-active compound A (C10H16) reacts with Pt/H2 to afford optically-active
compound B (C10H20). Ozonolysis of A and dimethyl sulfide reduction provides a single
compound C (C5H8O2), (R)-2-methylbutanedial [i.e., (R)-2-methyl butane dialdehyde].
What are the structures of A-C? Explain your reasoning.
2) (20 pts.) Design a synthesis of racemic epoxide 1 starting from 2-butyne and ethylene as
your only sources of carbon. You are obliged to use both of these sources of carbon in your
synthesis. All other reagents are available to you.

3) (4 x 5 pts. = 20 pts.) Circle the best answer(s) in each of the following.
a) The reagents, or pairs of reagents, that give a meso compound with (Z)-3-hexene.
|
|
OsO4/H2O2 |
cold, dilute KMnO4 |
1) peracid |
1) Cl2, H2O |
|
2) H3O+ |
2) aqueous NaOH |
b) The base(s) that will deprotonate 1-pentyne greater than 90%.
NaNH2 CH3CH2ONa CH3CH2CH2Li KNH2 NH3
c) The most highly oxidized structure(s).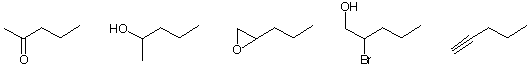
d) The complete hydrogenation of 3-hexyne (DHfo = +25.2 kcal/mol) is exothermic by 65.2
kcal/mol. What is the best estimate of the DHfo of n-hexane in kcal/mol?
90 39 -41 -89 + 41
4) (5 x 4 pts. = 20 pts.) In each of the following reactions, provide either the reactant, reagents,
or product as required. When reagents are missing, more than one reagent may be required to
prepare the product. Pay attention to stereochemistry.
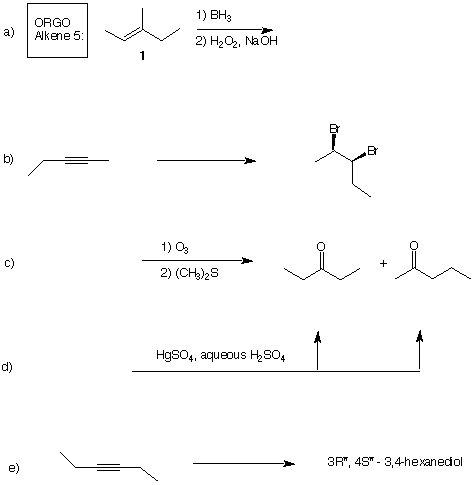
5) (20 pts.) Provide a mechanism for one of the following reactions. Use the curved arrow
formalism. Pay attention to stereochemistry where it applies.
a) The conversion of (E)-2-butene to 2-butanol (sec-butanol) via hydroboration.
b) The epoxidation of (Z)-butene via the halohydrin route.
c) The formation of 2-butanone (methyl ethyl ketone) by the mercuric ion catalyzed hydration
of 1-butyne.