CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, October 20, 2000
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important items are in bold.
There is a BDE Table on the last page (page 12) of the exam. A Periodic Table is on page 11.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets (pgs. 8-10). The work sheets
will not be graded.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (26 pts) ______
2. (20 pts) ______
3. (10 pts) ______
4. (20 pts) ______
5. (24 pts) ______
_______________________________
Total (100 pts)
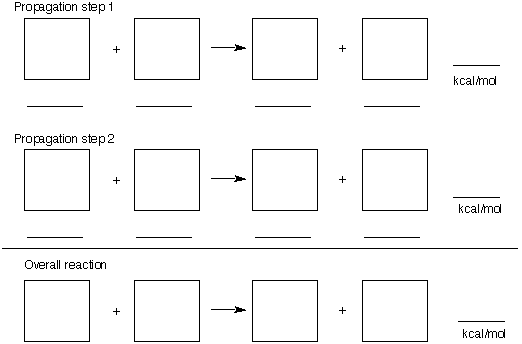
1) (26 pts.) Problem 1 of the alkane module of ORGO dealt with the free radical chlorination of
2,2-dimethylpropane (neopentane) to form 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane.
a) (10 pts.) Provide the two propagation steps and the overall reaction for this process. Place
the reactants and products in the appropriate boxes.

b) (8 pts.) Determine the heat of reaction for each of the propagation steps and for the overall
reaction given the typical BDEs in the BDE Table (page 12, last page). Place the values on
the appropriate lines under the boxes and at the end of each reaction. Show any
calculations below.
c) (8 pts.) Using Hess's Law and the overall reaction, determine the heat of formation of 1-
chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane given: DHfo (neopentane) = -40 kcal/mol; DHfo (HCl) = -22
kcal/mol. Show work.
Heat of formation of 1-chloro-2,2-dimethylpropane ---> __________ kcal/mol
2) (20 pts.) Draw the major product in each of the following reactions. Give a very, brief (a
few words) rationale.
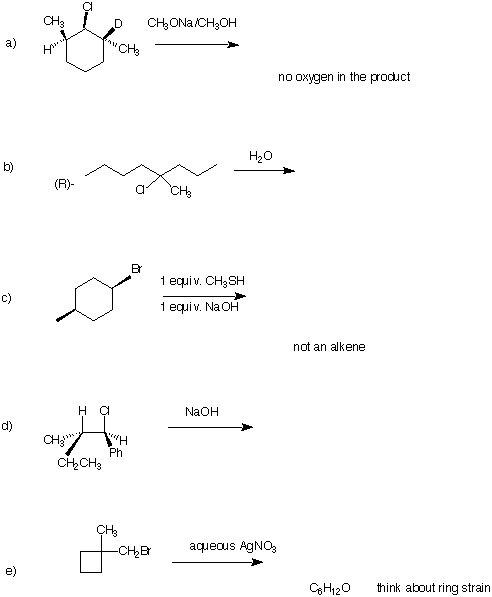
3) (10 pts.) L-Tartaric acid (R,R; "The Natural") has [a]D = +12o. When equal weights of
natural tartaric acid and (±)-tartaric acid are mixed in solution and the rotation is taken, what is the
value of [a]D. Show work.
4) (20 pts.) The diacid 1 may look achiral as drawn.
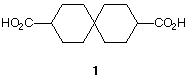
a) (7 pts.) Given your knowledge of the properties of allene dicarboxylic acid (PS4, #7),
Illustrate and explain why 1 is capable of resolution.
b) (7 pts.) Present schematically how you would attempt the resolution of this compound? A
few brief words of explanation are welcome.
c) 6 pts.) There are no asymmetric carbons in 1 and yet it is capable of resolution. What would
be the predicted sign of rotation of the (R)-enantiomer?
5) (24 pts.) Circle the best answer(s) in each of the following.
a) A mixture of enantiomers that has an enantiomeric excess (ee) of 40% contains how much of
the minor enantiomer?
|
70% |
80% |
50% |
30% |
20% |
b) The major monobromide to be formed from the free radical bromination of cyclohexene:

c) "One of these things [lactic acids] is not like the others, one of these things doesn't belong."
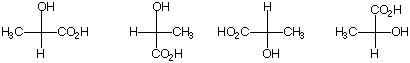
d) A 3/2 mixture of enantiomers displays [a]D = -30o. The rotation of the dextrorotatory
enantiomer is:
|
+300o |
-90o |
+150o |
-150o |
+60o |
-300o |
e) The dichloro compound(s) that will be achiral or racemic upon free radical chlorination of
(S)-1-chloro-2-methylbutane
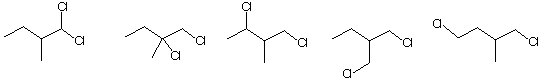
f) The terms that are associated with an SN1 reaction:
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
r