CHEMISTRY 220a
Friday, September 29, 2000
NAME (print): ___________________________________________________
TA:_____________________ Day:_________________ Time:__________
Take a few moments to look over the exam. Answer each question on the exam paper.
Important items are in bold.
The exam is 100 points with 10 optional bonus points. You can earn 110 points on a 100 point
exam.
Do all preliminary drawing or computations on the work sheets at the end of the exam. The
work sheets will not be graded.
The exam is 55 minutes.
STOP writing and hand in your exam when you are asked to do so.
REMEMBER: Neatness is to your advantage.
1. (20 pts) ______
2. (20 pts) ______
3. (20 pts) ______
4. (20 pts) ______
5. (20 pts) ______
6. (10 pts) bonus ______
_______________________________
Total (110 pts)
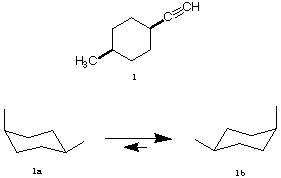
1. (20 pts) Compound 1 is a cis-1,4-disubstituted cyclohexane.

a) (5 pts) Place the substituents in their appropriate positions in 1a and 1b.
b) (5 pts) Figure 1b is present in 90.9%. Calculate DGo for this equilibrium. Show
work. DGo = -1.4 log10Keq; Keq = 1b/1a ]
c) (5 pts) What is the DGo value (kcal/mol) for the acetylene substituent? Show work.
[DGo = 1.7 kcal/mol for an axial vs. equatorial methyl group].
d) (5 pts) What term best describes the relationship between 1a and 1b?
2. (20 pts) The allyl cation [CH2=CH-CH2+] is a resonance stabilized carbocation. Draw a
molecular orbital representation of this species that clearly illustrates the molecular
orbitals and the resonance involved.
3. (20 pts) For the eclipsed and staggered conformations of 2-methylbutane viewed along the
C2-C3 sigma bond, draw a Newman projection of the least stable eclipsed and
staggered conformations. Place the appropriate energies in the Newman projections below.
[Use the circles as templates for the Newman projections.] Calculate the energy
(kcal/mol) of each conformation. Place your answer in the appropriate box. Show work.
[H/H, eclipsed, 1.0 kcal/mol; CH3/H eclipsed, 1.3 kcal/mol; C2H5/H, eclipsed, 1.1
kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, eclipsed, 3.0 kcal/mol; CH3/CH3, gauche, 0.9 kcal/mol; CH3/C2H5,
gauche, 1.0 kcal/mol.]

4) (20 pts; 4 pts. each) Circle the best answer(s) in each of the following problems.
a) The compound(s) with a net dipole moment

b) The incremental heat of combustion (DHo) for an unstrained methylene group is
-157 kcal/mol. What is the incremental heat of formation (D Hfo ) of an unstrained
methylene group? [D Hfo (H2O) = -68 kcal/mol; D Hfo (CO2) = -94 kcal/mol]
|
-162 |
+162 |
+157 |
-89 |
-5 |
+5 |
c) The alkane expected to have the largest heat of combustion.
|
n-pentane |
2-methylbutane |
n-hexane |
2,2-dimethylhexane |
2,2-dimethylpropane |
d) Compound(s) containing sp2 hybridized atoms
|
CH2O |
CH2=C=CH2 |
CH3CN |
BCl3 |
BeH2 |
e) Compound(s) that are deprotonated by NaOCH2CH3 (pKa (C2H5OH) = ~16)
|
CH3CO2H |
hexane |
NH3 |
HCN |
water |
5) (20 pts) The heat of formation (D Hfo) of n-octane is -49.8 kcal/mol and that of 2,2,3,3-
tetramethyl butane is -56.4 kcal/mol.
a) (15 pts) What is the difference in the heat of combustion of the two isomers? Illustrate
with a diagram.
b) (5 pts) Which isomer liberates more heat upon combustion?
6) (10 pts; 2 pts. each) Match the following luminaries in the history of organic chemistry
with their contributions: Baeyer, Kekule/Couper, Lavoisier, Liebig, Dumas/Laurent, van't
Hoff/LeBel. Enter the name on the line below..
Theory of combustion __________________
Tetrahedral carbon _______________________
Tetravalent carbon _________________________
Substitution theory _________________________
Baeyer strain theory ________________________
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets
Work Sheets