Ester 5:
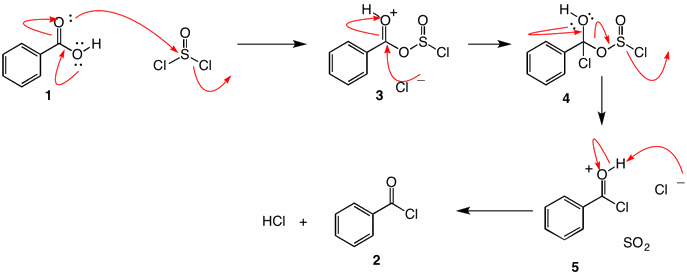
Solution: First a word about thionyl chloride. It is the equivalent of the bis-acid chloride of sulfurous acid [HOS(O)OH; pKa1 = 1.85]. Ostensibly chlorosulfurous acid has an even lower pKa. Therefore, the anion ClS(O)O- is an excellent leaving group. Intermediate 3 looks like an anhydride between benzoic acid and chlorosulfurous acid. Tetrahedral intermediate 4 collapses irreversibly to protonated benzoyl chloride 5 and sulfur dioxide and, ultimately, hydrogen chloride and benzoyl chloride. The two gaseous byproducts, sulfur dioxide and hydrogen chloride, help drive the reaction to completion. Although it looks like one starts with stoichiometric amounts of reactants, in practice thionyl chloride is usually used in excess. Distillation readily separates excess thionyl chloride (bp. 79oC) and benzoyl chloride (bp. 197oC). Often pyridine is employed as a catalyst. It generates the anion of the carboxylic acid, which is more nucleophylic than the carboxylic acid. Pyridinium hydrochloride increases the concentration of free chloride for the transformation 3 ---> 4.
