Ester 4:
Problem:
![]()
Solution:
![]()
This procedure is known as the Fischer esterification. A carboxylic acid (acetic acid) and an alcohol (primary or secondary) react to form an ester and water in an equilibrium reaction. The reaction is auto-catalytic but a catalytic amount of a strong acid (p-toluenesulfonic acid) speeds up the reaction. For stoichiometric amounts
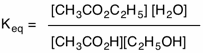
of these two reactants at equilibrium there is about 65% of each product and 35% of each reactant which translates to Keq = 3.4. To increase the amount of ester one can apply LeChatelier's Principle: remove product (ester or water) or use a reactant in excess. Imagine that acetic acid is expensive while ethanol is not. Using a ten-fold excess of ethanol over acetic acid will drive the reaction to the right giving each product in 97%. In the formation of water, what is the source of the oxygen atom? Does the oxygen come from the carboxylic acid or the alcohol?