Alkene 7:

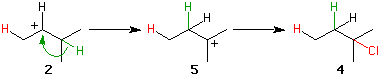
Secondary carbocation 2 can also rearrange. The green hydrogen and its electron pair migrate (hydride
migration) to the secondary site, creating the more stable tertiary carbocation
5. Capture of chloride ion provides 4. Note that the arrow
head in 2 points to the carbocationic center. This process is distinguished
from the deprotonation of the carbocation 2 to produce 2-methyl-2-butene
6 and a proton.

In this case, the arrow head points to the carbon-carbon bond where the double bond is formed. How do we know that the formation of carbocation 5 is formed by hydride migration as opposed to deprotonation of carbocation 2 followed by Markovnikov protonation to form 5? Think about this a moment, then click here to go on.