Chem 220a
Problem Set 7
Chapter 8
Due: Monday, October 25, 1999
The alkene module of ORGO has a direct bearing on the solution of
the problems in this problem set. You are
strongly advised to due the exercises.
[https://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids/index/index.html] The
ozonolysis module in the Study Aids will be of help.
[https://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids/ozonolysis/Oz.html]
When [!] appears in the following problems, an important piece of
information has been established for the
determination of the structure. The absence of [!] does not mean
the information is unimportant.
|
1) An unknown compound A (C7H12) reacts with
H2/Pt to give B (C7H14)[!]. Ozonolysis of A
forms 6-oxoheptanal (i.e., 6-keto-n-
heptaldehyde)[!]. When compound A reacts with
HCl in the presence of a peroxide (be careful), a
single compound C (C7H13Cl) is formed.
However, when A reacts with HBr in the
presence of a peroxide, two compounds
(C7H13Br) D and E are formed. What are the
structures of A-E? Show your reasoning.
|
 Vladimir Vasilovich Markovnikov
(1838-1904)
Vladimir Vasilovich Markovnikov
(1838-1904)
|
2) The reaction of (Z)-4-octene in the presence of Br2/H2O gives
compound A, C8H17BrO. Is A racemic or optically active? Exposure of A
to aq.
NaOH affords B, C8H16O. B is also formed from (Z)-4-octene by
reaction with m- chloroperbenzoic acid [!]. What are the structures
of A and B?
Show your reasoning.
3) An unknown compound A (C10H20) reacts with Br2 in an inert
solvent to form a meso compound B[!].
The reaction of A with KMnO4 or OsO4 gives a d,l-diol C [!].
Catalytic hydrogenation of A gives n-decane.
What are the structures of A - C? Show your reasoning.
4) Ozonolysis of A (C6H12) gives a C5 aldehyde B and aldehyde C.
Oxymercuration of A provides a mixture of
diastereomeric alcohols D and E (C6H14O) [!]. Two other
structural isomers of A, namely, (Z)-F and (E)-F, react as follows.
Hydroboration of (Z)-F forms D and hydroboration of (E)-F forms
E [!]. Ozonolysis of either isomer of F gives the same
aldehyde G and ketone H [!]. Compounds A and (E)-F and (Z)-F
give 3-methylpentane upon catalytic hydrogenation. What
are the structures of A - H? Show your reasoning.
5) An unsaturated aldehyde A, C10H18O; has [a]D25 = + 11.5o. The
reaction of A with ozone gives equal
amounts of 2-propanone (acetone) B and C, (R)-3-methylhexandial
(i.e, ...hexane-di-aldehyde). Draw the
structures of B and C accurately? At this point what are the two
possible structures of A?
Hydrogenation of A gives the aldehyde (R)-3,7-dimethyl-octanal D
(C10H20O, octane aldehyde). Draw
the structure of D. How does the hydrogenation experiment
distinguish between the two possible
structures of A ? What is the structure of A?
|
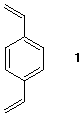
6) Polystyrene dissolves readily in organic solvents.
When styrene is polymerized under radical
conditions in the presence of 1% of 1,4-
divinylbenzene 1, a polystyrene is formed that
does not dissolve in organic solvents.
It is more rigid than the normal polystyrene.
Illustrate and explain.
|
|
7) When olefins such as styrene and propene are polymerized by
radical means, they give atactic polymers. In
an atactic polymer, the phenyl group (polystyrene) or the methyl
group (polypropylene) are randomly
distributed on either side of the zig-zag carbon chain. Draw an
atactic polypropylene chain. The Ziegler-
Natta catalyst (a Ti-Al catalyst, nothing to do with me) produces
isotactic (all methyls on the same side of the
chain) polypropylene. Draw an isotactic polypropylene chain using
a zig-zag carbon chain. The isotactic
chain does not exist in this conformation. It is helical. Why? Are
the chains all of one handedness?

