|
Chem 220a
Problem Set 5
Chapter 6
Due: Monday, October 11, 1999
1) Study the problems 2-4 in the Alkyl Halides module of
ORGO.
2) Learn about "Degree of Unsaturation" at
https://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids/unsaturation/unsat.html
We will be using this concept in class. The text uses a
formula. I think the website method is easier. Try this one:
C12H10BrClN4OS.
3) Compound A, C5H12,
undergoes free radical chlorination to give four
monochlorination compounds. [A pair of enantiomers is
counted as a single compound.] What is the structure of
A? Which structures are achiral? Which structures are
racemic? Do any of them exist as single enantiomers? Name
them. For the racemic compounds, draw the enantiomers and
provide R,S-configurations.
|

Biot examines Pasteur's tartrate crystals
|
4) When 2-bromo-1,1,1-trideuteriopropane is heated with
C2H5ONa in ethanol, the major
olefin formed is CH2=CHCD3. Why? What is the
structure of the minor olefin?
5) When (2S,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylpentane (1) is heated in
methanol, (2R,3S)-2-methoxy-
3-methylpentane (2), (2S,3S)-2-methoxy-3-methylpentane
(3) and 3-methoxy-3-
methylpentane (4) are formed. Why are the enantiomers of
2 and 3 not formed? Are
2 and 3 necessarily formed in equal amounts? Why or
why not? Is 4 optically active?
Why or why not?
6) When (2R,3S)-2-bromo-3-methylhexane (1) is heated in
C2H5ONa/C2H5OH,
alkenes
C7H14 are formed. What is the structure of
the major alkene 2? How is it formed?
Why is its geometrical isomer not formed? What is the structure of
the major alkene
derived from the enantiomer of 1? Illustrate. What is the
structure of the major
alkene derived from a diastereomer of 1? Illustrate.
7) When Paul Walden (1863-1957) studied the reaction of
(+)-chlorosuccinic acid [HO2CCH2CHClCO2H] in dilute aqueous
base, (+)-malic acid was formed [HO2CCH2CH(OH)CO2H]. Both
compounds were found to have the same relative configuration.
Substitution occurred without inversion. How is this possible?
[Hint: no inversion is the same as two inversions.] When
(+)-malic acid was treated with PCl5, chlorosuccinic acid was formed
by an SN2 inversion. What was the sign of rotation of this sample of
chlorosuccinic acid?
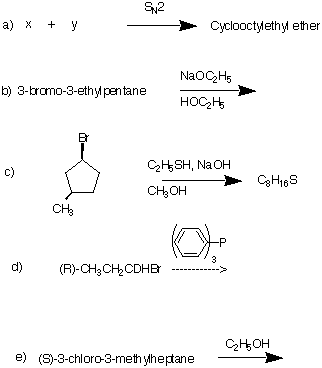
8) Provide the major product in each of the following reactions.
Explain and/or illustrate.