1. Draw the 1H NMR spectrum for the major and minor free radical monobromination products of
isobutane. Place the chemical shifts in the correct order and be sure the coupling is correct. Explain your
answer.
2. Compound A (C4H8O2) has the following 1H NMR spectrum: d 1.15 (3H, t, J = 7 Hz), 1.95 (3H, s)
and 4.05 (2H, quartet, J = 7 Hz). What is the structure of A? Why doesn't methyl propionate fit the
data? Explain.
3. An unknown compound A (C6H12) forms a single compound B upon ozonolysis and zinc reduction.
The 1H NMR spectrum of B shows a singlet at d 2.1 and its decoupled 13C NMR displays two singlets,
one of which is at ~204 ppm. What are the structures of A and B? Explain.
4. Two bottles in a laboratory have the same label, "C5H10Br2". The 1H NMR spectra of the contents of bottles A
and B are as follows: A: d 3.4 (4H, s) and 1.0 (6H, s). B: d 2.4 (4H, quart.) and 1.0 (6H, t). What are the structures of
A and B. Explain.
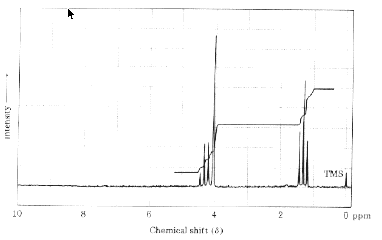
5. The 60 MHz 1H NMR spectrum of one of the products of monochlorination (compound B) of compound A from
problem 2 is shown below. How many protons are in each of the two regions of the spectrum? What will the spectrum
look like at 500 MHz? Draw it. How will the coupling constants be affected in going from 60 MHz to 500 MHz spectrum?
What is the structure of compound B?

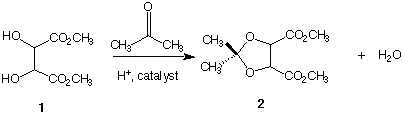
6. Both meso and racemic dimethyl tartrate 1 contain three different kinds of protons with different chemical
shifts. Which ones are prone to variable chemical shifts? What technique is used to locate these protons
in a given spectrum? When either diastereomer of 1 is treated with acetone in the presence of an acid
catalyst, a 5-membered ring (an acetal) 2 is formed in addition to water. [No need to worry about the
details of this reaction here.] When this reaction is conducted on (±)-1, the spectrum of (±)-2 contains
three singlets in a ratio of 3:3:1. When meso-1 is converted into meso-2, the spectrum of meso-2 contains
four singlets in a ratio of 6:3:3:2. [Hints: Note that the two methyl groups derived from acetone lie in a
plane that is perpendicular to the plane of the ring. A molecular model will help.]
7. Predict the number of singlets in the decoupled 13C NMR spectrum of meso-2 and (±)-2 in problem 6.
Explain your reasoning. If the decoupler were turned off, what would be the multiplicity of the signals in
(±)-2?
8. 1-Chloro-2,2-difluoropropane has the following 1H NMR spectrum: d 1.75 (3H, t, J = 18 Hz) and 3.63
(2H, t, J = 18 Hz). Why do equivalent protons show such large couplings?