Problem Set 9
Chem 220
Due : Monday, November 10, 1997
Chapter 12
Study the examples in Alkynes on ORGO before doing this PS. Answer the questions
before looking at the answers.
1. Compound A (C10H20) reacts with Cl2 to form B (C10H20Cl2). Treatment of B with t-
BuOK/t-BuOH gives (Z)-5-chloro-5-decene C. What are the structures of A and B and
show how they are formed?
2. Design a synthesis of (Z)-3-hexen-1,6-diol from organic compounds having two or fewer
carbons.
3. Compound A (C8H14) reacts with NaNH2 to form B (C8H13Na). A is formed
from B when B is added to water. B reacts with C (C6H13Br) to form D
(C14H26). Treatment of C with Mg in ether followed by addition of ethylene
oxide forms n-octanol. When D is exposed to Li/NH3, compound E (C12H24) is
formed. Bromination of E gives a meso compound F. What are the structures of A-
F and show how they are formed?
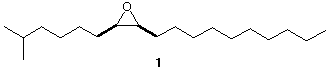
4. Disparlure (1), is the sex attractant of the female gypsy moth. It is an optically active
compound. Show how to synthesis racemic 1 from 5-methyl-1-hexene, 1-octanol, and
any other carbon compound.

5. Demonstrate your knowledge of acid/base reactions and resonance to show how 2-hexyne is
converted to 1-hexyne (SHK, pg. 308). 1,2-Hexadiene (CH3CH2CH2CH=C=CH2) is an
intermediate in the reaction. Why is the reaction driven to the right with stoichiometric base and not
catalytic base?
6. Why is (Z)-cyclohexene stable and (E)-cyclohexene and cyclohexyne are not?
7. Compound A, (C4H6) reacts with catalytic HgSO4 in the presence of aqueous sulfuric acid to form
B. Compound A does not react with NaNH2 in NH3 at -33 oC. 2,2-Dimethyl-3-pentanol
rearranges in the presence of sulfuric to give C (C7H14). Ozonolysis of C gives two ketones: D
(C3H6O) and B. What are the structures of A-D and how are they formed?