- Chem 225b - Comprehensive Organic
Chemistry
Problem Set 4, Stereochemistry
Chapter 5
Due: Monday, February 18,
2008

|
The
Borremean Rings
Versions of this symbol date to the time
of the Vikings.
In the 15th century, it was apparently the symbol of a
tripartite alliance of the Milanese families Visconti,
Sforza and Borromeo via intermarriage. Break any (wedding?)
ring and the others separate, hence the alliance is broken.
The rings form a chiral
object (left) that are not
superimposable on their mirror
image. A set of Borremean rings
has been used as the logo for a certain refreshment that
extols purity, body, and flavor. Is the sense of chirality
of the two sets of Borremean rings the same or different?
For some other discourses on chirality, see:
Potpourri
The Figure 8
Knot
Gentlemen's
Neckties
Molecular
Knots
|

|
Read the stereoisomers
module in the StudyAids and do the
exercises. There is no need to record answers on your homework.
Don't forget the Chirality
of Shells (Powerpoint).
|
1. When (R)-sec-butylbenzene,
a.k.a 2-phenylbutane, undergoes free radical chlorination,
four monochloro constitutional isomers are formed, the
phenyl ring remaining intact. What are these structures?
Draw them. Be explicit as to diastereomers, enantiomers,
racemates, etc.
|
|
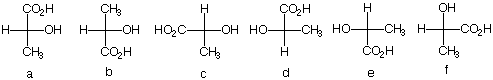
2. There are twelve possible Fischer
projections for a given enantiomer of lactic acid. Why?
(S)-(+)-Lactic acid, the cause of cramping during vigorous,
anaerobic
physical exercise, was isolated
from human muscle by Berzelius.
Which of the following Fischer projections represent
(S)-(+)-lactic acid?
|
|
3. A mixture of enantiomers has [α]D
= -78o. If the rotation of the pure
dextrorotatory enantiomer is [α]D =
+104o, what is the composition of the
mixture?
|
|
4. a) 1,2-Dibromoethane is optically
inactive yet it has a dipole moment. Explain and
illustrate.
b) meso-Tartaric acid exists in three staggered
conformations, none of which has a plane
of symmetry. Yet the compound is
optically-inactive. Explain and illustrate.
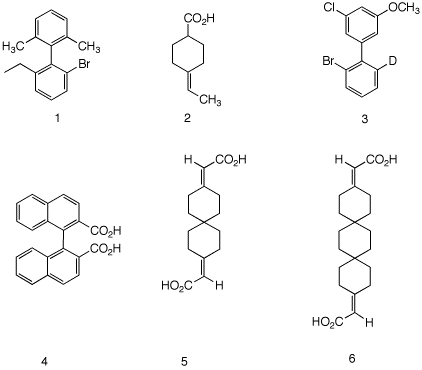
5. Which of the compounds on the right are, in principle,
capable of resolution? Explain and illustrate.
6. (S)-α-Phellandrene
([α]D
= +86o) is a monoterpene with the characteristic
fragrance of dill. Monoterpenes, which are C10
compounds, are dimers of two identical, branched
C5 compounds. (S)-α-Phellandrene
reacts with 2 moles of hydrogen gas in the presence of Pd to
give two cyclohexanes A and B, both of which
have the formula C10H20 and both of
which are optically inactive. Compound A has an
energy difference of 0.4 kcal/mol between its two chair
conformations while compound B has a value of 3.8
kcal/mol for the same equilibrium.
a) Explain the loss of optical activity, the energy
differences, and identify the structures A and
B.
b) Circle the two C5 units of (S)-α-phellandrene
that dimerize. Ignore double bonds and
stereochemistry.
|
|
|
5.
(R)-α-Phellandrene
has been reported to have a specific optical rotation of
-217o. This observation suggest that the sample
of the enantiomer used in problem 6 above is contaminated.
Assume that the contaminant is the (R)-enantiomer and that
the (S)-enantiomer is pure. What percentage of each
enantiomer is present in the sample of problem 6? Show
work.
|

