|
1. Reading assignments: a)The alkene module in ORGO. How do I approach solving problems
like #2--5? Here
is a step-by-step analysis of #2
PS7 from F2000. |
Vladimir Vasilovich Markovnikov (1838-1904) |
|
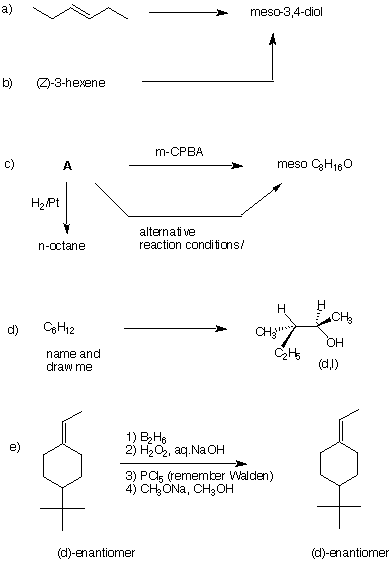
3. Compound A, C7H12, affords a single ketoaldehyde B upon ozonolysis and dimethyl sulfide reduction. Hydrogenation of A gives methylcyclohexane and the reaction liberates 27.0 kcal/mol of heat. Treatment of A with HBr in the presence of peroxide gives two compounds, C and D. Compound C reacts with C2H5ONa/C2H5OH to give E while under the same conditions, compound D gives mainly A and some of compound E. Ozonolysis of E gives a single dialdehyde F. What are the structures of A-F? Explain and illustrate. Pay attention to stereochemistry. |
4. Compound A reacts with
Br2 in CCl4 to give B. The
intermediate in this reaction (C) is a meso
species. Ozonolysis of A affords only propanal
(propionaldehyde). What are the structures A-C?
Explain and illustrate. Pay attention to
stereochemistry.
5. Optically active hydrocarbon
A reacts with 2 molar equivalents of hydrogen to
produce compounds B and C, both of which
are optically inactive. Ozonolysis and dimethyl sulfide
reduction of A affords pyruvaldehyde D
(C3H4O2) and
(S)-isopropylsuccindialdehyde E (tartaric
acid = 2,3-dihydroxysuccinic acid). What are the
structures A-E? What is the sign and value of the
optical rotation of A? Explain. [Note:
B and C cannot be distinquished from one
another with the information presented.]