August Wilhelm von Hofmann
(1818-1892)
Royal College of Chemistry (1845)
Berlin (1865)
1. Learn how to determine the Degree
of Unsaturation of a compound from its formula. We will
be using this concept in class. The text uses a formula. I
think the website method is easier. Try this one:
C12H17Br2ClN2O2S.
2. Do problems 2-4 in the Alkyl Halide module in
ORGO. They
need not appear on your homework.
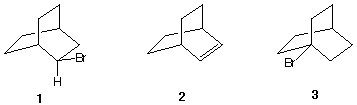
3. Construct a diagram [like the one here]
that interrelates the heats
of formation and the heats of hydrogenation (Table 7-1,
pg. 307) of (E)-2-hexene, (Z)-2-hexene and
n-hexane, and the standard state. Provide numerical values.
Do your values for the heats of hydrogenation make sense
with relevant data in Table 7-1, pg. 307?
4. Determine the heat of formation of 2-methyl-2-butane
given the data provided in Table 7-1, pg. 307, and the
heats
of formation provided in the Study Aids.

Aleksandr Mikhailovich Zaitsev
[Saytzeff (German)]
(1841-1910)
University of Kazan