Problem Set 4
Chapter 5
Due: Monday, October 9, 2000
|
Biot examining Pasteur's tartaric acid crystals |
Michelangelo-The Creation of Man 1508-12 Sistine Chapel |
1) Read the stereochemistry module in the StudyAids and do the exercises. There is no need to record answers on your homework. http://classes.yale.edu/chem220a/studyaids.html#Stereoisomers
|
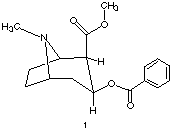
2) Structure 1 on the left is cocaine {[a]D = -18o}. Provide the R and S configuration for each of the stereogenic centers. Theoretically, there are a total of 16 stereoisomers of this structure including 1. In, actuality, only 8 stereoisomers are capable of existing. Explain. |
 |
|
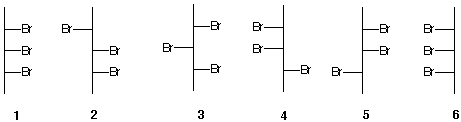
3) For the 2,3,4-tribromopentanes (1-6) shown below, which ones are identical, achiral, chiral, or enantiomers. |
 |
|
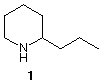
4) In 1886, Albert Ladenburg, synthesized the Socratic poison, coniine (2-propylpiperidine (1)), in racemic form. He resolved the racemate into its enantiomers using the reverse of the technique employed by Pasteur ~25 years earlier. a) What did Ladenburg do? b) Was he able to predict which enantiomer he would isolate in his very first experiment? Elaborate. c) The enantiomer of coniine present in hemlock (Conium maculatum L., Umbelliferae ) is (S)-(-)-coniine, [a]D = -18o. Draw the (S)-enantiomer of coniine. d) Assume that Ladenburg obtained a sample of coniine on his first resolution that had [a]D = -12o . What should he have concluded about his resolving agent? How much of each enantiomer would have been in his sample? |
Albert Ladenburg (1842-1911) |
 |
|
5) Structure 1 represents limonene, a fragrant constituent in lemon grass. a) Draw (R)-(+)-limonene? Is the rotation obvious from the (R)-configuration? b) (R)-(+)-Limonene is reduced in the presence of two equivalents of H2 and a catalyst to a mixture of two compounds (C10H20). c) What are their structures? d) Is either one optically active? Explain. e) One of the reduction products is more stable in one of its chair conformations that its stereoisomer is in either of its chair conformations. Which one is it? f) What is the difference in conformational energy in e). Calculate and explain? |
|
|
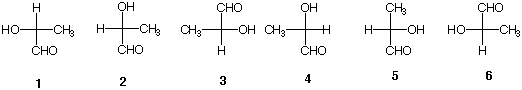
6) Which of the following Fischer projections are identical to one another? |
|
|
|
7) In 1874 van't Hoff predicted that allenes bearing two different pairs of substituents could be resolved. This prediction was confirmed independently by two different research groups after 59 years (1935). In what way must the pair of two different groups (say, A, A, B, and B) be substituted for the hydrogens on allene? Explain. [One pair of groups may, in fact, be hydrogen.] What kind of groups would be useful to illustrate van't Hoff's prediction? |