|
1) The new NMR module for Chem 220a is an interactive exercise that will help you learn about 1H and 13C NMR. If you study all the 12 compounds in the Novice Level in the order 11, 12, 2, 3, 7, 1, 10, 6, 8, 4, 5, 9 they will be in an ascending order of difficulty. Try to avoid the solutions until you are truly in need. A problem on the final exam will be derived from this exercise. 2) The label on a bottle in a laboratory reads "C4H8Br2". The 1H NMR spectrum of the contents of bottle A display: d 1.87 (s, integral = 3) and 3.86 (s, integral = 1). What is the structure of A? Explain. |
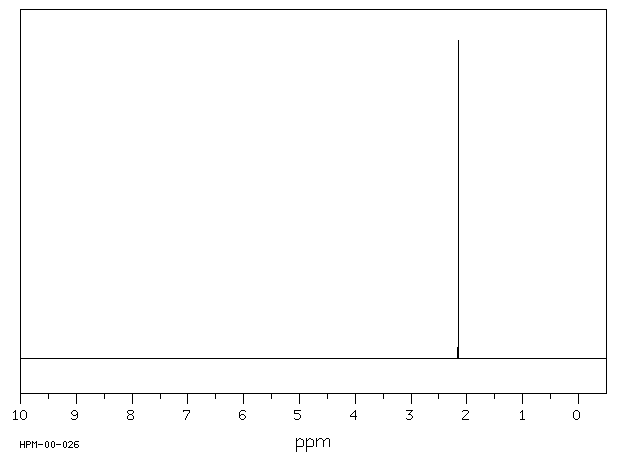
A low resolution 1H NMR spectrum (~30 MHz) (http://www.varianinc.com/nmr/) |
|
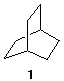
3) Show how you would distinguish, one from another, the free radical monochlorination products of [2.2.2]-bicyclooctane 1 by 13C NMR spectroscopy. 4) This problem needs to be done on-line. Compound A reacts with 2 equivalents of C2H5MgBr to give B, whose 1H NMR spectrum is at the upper right (the low field signal disappears in the presence of D2O) and C (C6H14O). Treatment of C with H2SO4 gives three compound D, D', and D'' (C6H12). D' (E) and D'' (Z) are geometrical isomers. Ozonolysis and dimethyl sulfide reduction of D affords E and compound F. What are the structures of A-F? Explain and illustrate. |
 |
|
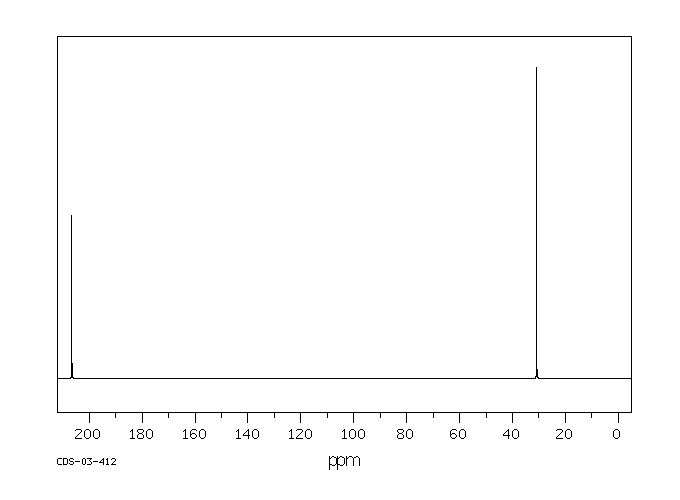
5) This problem needs to be done on-line. The ancient tree, Gingko biloba, is claimed to date back to the age of the dinosaurs (65-150 million years ago). My neighbors have a female tree in their yard that drops its rancid fruit this time of the year. [Here you can get the opinion of 4th graders on the smell of the fruit expressed as only they can.] Butanoic acid (n-butyric acid) has the smell of rancid butter. It is one of the odiferous components of the fruit. I brought some of the fruit into the lab. Martha Sarpong (one of our TAs) crushed the fruit, extracted the pulp with hot water, extracted the cooled aqueous solution with ether, and isolated a liquid. The 1H NMR spectrum and the 13C NMR spectrum, which were recorded by Jing Zhao, are provided. Examine the 1H NMR spectrum of the extract and you should be convinced that there is more here than n-butyric acid (butanoic acid) present. Note the two triplets at high field of unequal intensity. Expand the region around d 2.25. It contains two triplets for -CH2CH2CO2H. Look at the 13C NMR spectrum. How many -CO2H carbons are there? The remaining eight signals are upfield. Three of them belong to n-butyric acid, the remaining five belong to what normal chain carboxylic acid? Think about it, then check here and here. Redraw the upfield portion of the spectrum and assign each signal to one of the two carboxylic acids. 6) Compound A (C6H12O, 4 singlets in the 13C NMR spectrum) reacts with LiAlH4 to afford B (C6H14O). Treatment of B with H2SO4 at 100 oC gives compound C. Ozonolysis of C provides a single compound D whose 1H and 13C spectra are shown below. What are the structures of A-D? Explain and illustrate. |