Chem220 - Organic Chemistry
Problem Set 2
Chapter 3: Acids and Bases: Curved Arrow Notations
Due: Monday, September 26, 2011

Josiah Willard Gibbs
(1839-1903) |
J. W. Gibbs - b. New Haven, CT. Awarded 1st US PhD in the sciences (Yale, SSS, 1863). Developed the concept of free energy (ΔG) and the chemical potential. Gibbs spent his entire career at Yale.
.
G. N. Lewis - b. Weymouth, MA., Professor UCBerkeley. Developed concept of the covalent bond, dot structures and "Lewis" acids and bases.
|

Gilbert Newton Lewis
(1875-1946)
|
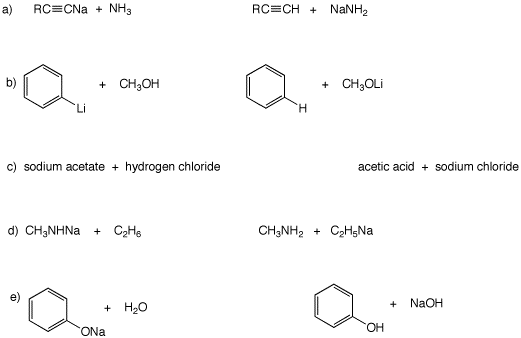
1. With the aid of the pKa table, determine the Keq for each of the following reactions. Place an equilibrium arrow between the second and third structures that reflects the value of Keq, i.e.,  Explain your results.
Explain your results.
2. Determine the Gibbs free energy at 25 oC of the reaction NH2- + H+ -------> NH3. Recall -ΔGo = RT ln Keq (-ΔGo = 2.3RT log Keq), where R = 1.98 cal/mole-oK. The pKa table will be of help.
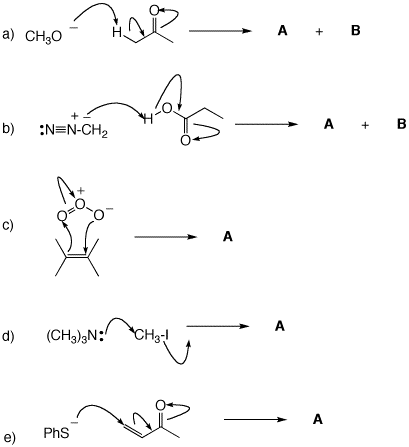
3. For each of the following mechanisms, illustrate the structures of the products. If a resonance structure applies, illustrate the resonance.
4. Phenol is converted to its anion by washing soda (Na2CO3) but not by baking soda (NaHCO3). pKa's: H2CO3, 6.4; HCO3-, 10.3. Explain and illustrate. What is the value of Keq for the reaction of phenol with the stronger of these two Brønsted base?
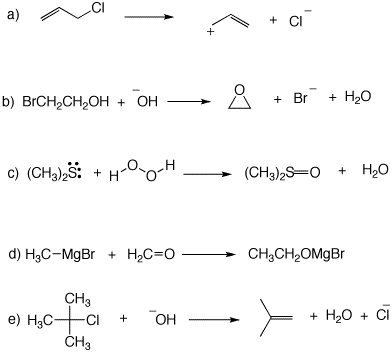
5. Using the curved arrow formalism, illustrate how the reactants in the following reactions are converted to products. You may have to redraw somes structures to show bonds and/or electron pairs.