Problem Set 2
Chapter 15
Due: Monday, January 31, 2005
|
|
See Pericyclic Reactions in the StudyAids for a review on conjugation, cycloadditions, and electrocyclic reactions. Electrocyclic reactions are not covered in the text. |
|
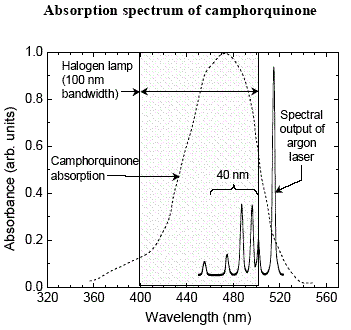
1.
a) What kind of spectrum is it? b) What is the λmax of CQ? c) What concentration (mg/mL) of CQ is required to produce this spectrum [εlog=1.49 at λmax ]? [Assume a 1 cm cell.] d) What color light does CQ absorb? e) What color is CQ? f) What color are the glasses that you wear when the dentist zaps you with the "light gun"? Why are they that color? |
 |
|
2. Draw the structures of the Diels-Alder
adducts arising from 1,3-pentadiene and
CH3CH=CHCO2CH3 under the
conditions described in the Table. Provide a transition
state model for example 2. Which Examples give the same
racemic product? Explain. 1 E E endo 2 E Z endo 3 Z E endo 4 Z Z endo 5 Z E exo |
|
3. In each of the problems below, provide the missing information, i.e., conditions, product, reactant, etc. Also, explain the reason for your choice.
|
|
4. Compound A is colorless an it is devoid of absorption in the range 200-800 nm. Thermolysis of A affords B, which absorbs at 227 nm. When B is heated with maleic anhydride, compound C is formed, which has five singlets in its broadband decoupled 13C NMR spectrum. Compound C displays vinyl hydrogens in its 1H NMR spectrum. What are the structures A-C? Explain and illustrate. |



