|
1. Study #2 and #3 in the Alkyl Halide module and #1 in the Ether module in ORGO. 2. Achiral compound A (C8H14) is inert toward hydrogen in the presence of a catalyst. Compound A can and does form two, and only two, monosubstitution products upon free radical chlorination. One of these products, B, is achiral while C is a racemate. Compound B is inert toward C2H5ONa/C2H5OH while compound C affords achiral compound D. a) What are the structures of A-D? Show your reasoning. b) What is the ratio C/B in the chlorination of A? Show work. 3. When 1-bromo-2,2-dideuteriocyclohexane is heated in the presence of sodium ethoxide in ethanol, the major product formed is a cyclohexene. What is its structure and why is it formed? |
|
|
4. When (2S, 3S)-2-chloro-3-methylheptane (A) is heated in the presence of CH3ONa/CH3OH, two alkenes B (opt. active) and C are formed. When the (2S, 3R) diastereomer of A is subjected to the same reaction conditions, B' and D are formed. a) What are the structures of B,B',C and D? b) Is B or C the major product? c) Is B' or D the major product? d) How do C and D differ? e) How do B and B' differ? f) Illustrate the mechanism for the formation of B,B',C and D. |
|
5. What are the structures of A in a)-d)? Explain and provide mechanisms for each of the five reactions.
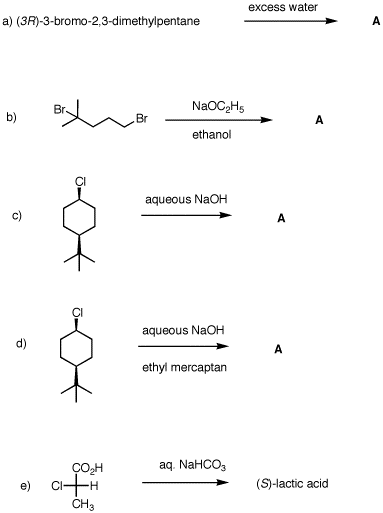 |
|
6. Bromide B is the predicted major product derived from A. Bromide G is one of two conceivable structures derived from F. Bromide B is not the other one, nor is it a minor product from the bromination of A. Only G can be found. What are the structures A-G? Explain and illustrate.
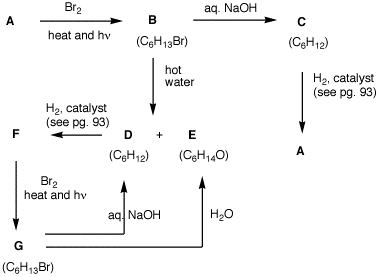 |