|
The topic of oxidation levels of
organic compounds is addressed in passing on pg. 458. We
will consider the issue in more detail as described in
Oxidation
Levels.The alcohol module in
ORGO
will give you a good review of some of the fundamental
reactions discussed in class and in Chapters 10 and
11. 1. Alkyne A undergoes hydration in the presence of HgSO4 to give a single compound B. Treatment of B with methyl magnesium bromide produces C, which is readily dehydrated with H2SO4 to form two possible products, D (major) and E(minor). Ozonolysis of E followed by dimethyl sulfide reduction forms B and F. Ozonolysis of D gives propionaldehyde G and a symmetrically substituted ketone H. What are the structures A-H? Explain and illustrate. |
Victor Grignard (1871-1935) |
|
2. Compound A, C12H22O2, reacts with two equivalents of Grignard reagent B to form C (C9H18O) and D (C5H12O). Compound C reacts readily with hydrochloric acid to form H (C9H17Cl), which upon exposure to aq. NaOH gives principally E (C9H16). Ozonolysis of E gives two ketones: cyclohexanone and F. Compound D was found to be identical with the product G formed from the following sequential reactions with 2-propanol: PBr3, Mg/ether, and ethylene oxide. What are the structures of A-H? Explain and illustrate. |
|
3. Due Web of Reactions I. |
|
4. Design a synthesis of 5-nonanol from 2-butyne and an ester of two or fewer carbon atoms. |
|
5. How many grams of potassium dichromate are required to oxidize 75 grams of cyclopentanol to cyclopentanone. Show work. |
|
6. Redo #6e PS7 using tosylate formation for the third chemical step. What product is formed? Explain why this change in conditions changes the answer. |
|
7. More than one equivalent of HCCM (M = Li, Na, MgBr) is required to convert estrone to ethynyl estradiol even though the stoichiometry of the reaction is one estrone to one acetylide. Explain. Only one stereoisomer is formed in this reaction. There is no compound having the non-phenolic hydroxyl dotted. What is the role of the quaternary methyl group in making this reaction highly selective? |
|
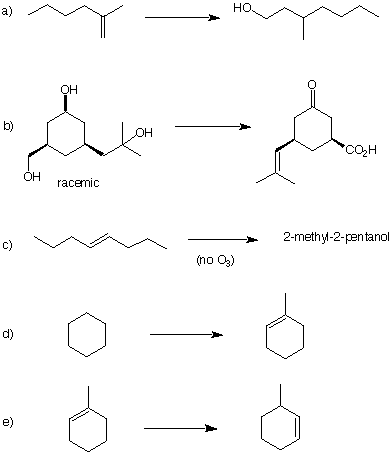
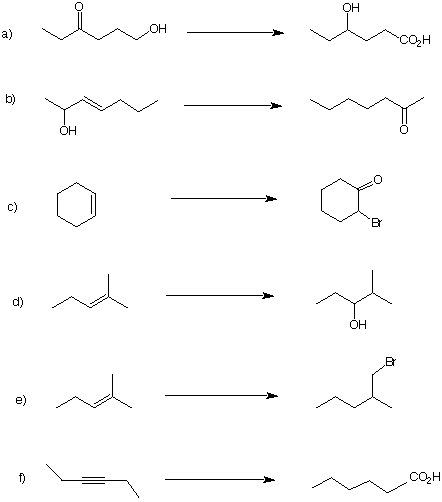
8. In each of the following reaction
sequences, list the reagents necessary to complete the
transformation. Each one requires several steps. Select
conditions that are the most selective, i.e., minimize
isomers. |
|
9. Two optically active compounds (C10H16) A and B each liberate 57.2 kcal/mol of heat upon catalytic hydrogenation in the presence of platinum. Compound C, formed from A, is optically inactive while compound D, formed from B, is optically active. Both A and B, upon oxidation with warm, concentrated KMnO4 affords only compound E, (R)-methylsuccinic acid. Explain and illustrate. [Note: Remember the Walden cycle discussed in class.] |
|
10. In each of the following chemical transformations, determine if the the overall reaction is an oxidation, reduction or if it is electroneutral. Give a brief explanation. No reagents are required.
|